The Hidden Value of Scrap Metal: Why Local Recovery Matters
May 28, 2025
For this edition of our Making Circularity Stick series, we explore the world of scrap metal processing with Emily Molstad, CEO of our portfolio company VALIS Insights.
Emily Molstad, CEO of our portfolio company, VALIS Insights, and Aly Bryan, Investor on the Closed Loop Ventures Group team at Closed Loop Partners, explore how the metals processing system in the U.S. is misaligned––with high value scrap going to low value applications far away from where it’s recovered. The discussion explores the core reasons for this misalignment, and how our portfolio company, VALIS, is supporting processors to make more money with local processing while keeping copper, nickel, aluminum and many other metals in domestic circulation.
There has never been a better time to strengthen metals circularity, and Closed Loop Ventures Group is energized to continue to support the VALIS team.
Aly: One of the things that’s always struck me about scrap processing in the U.S. is the amount of scrap that’s exported. After all, there are valuable materials in those exports! Copper, nickel, aluminum. Why is it that valuable scrap gets sent overseas today?
Emily: One of the biggest challenges in scrap metal is the fragmented nature of the secondary metals processing system––which produces alloys or remelts metal scrap to create new products. While there are several, multinational organizations operating in the space, huge volumes of scrap metal go through a localized system of processors within a region. This makes sense, since it wouldn’t be economical to lug every end-of-life car to a centralized processing facility. So instead, they’re processed at smaller facilities closer to consumers. However, those regional processors have long-standing customer relationships, which, historically, have been overseas, in areas where labor costs for manual sortation are low. This means that a lot of high value metals from local manufacturers are transported long distances and become commodities elsewhere, instead of being recaptured within the domestic market. This has remained the status quo for a long time, as scrap processors often prefer to sell how they’ve always sold, with hesitancy to take advantage of changing market conditions that allow them to operate more profitably while supporting national security of metals and minerals.
Aly: What do you mean by changing market conditions?
Emily: Let’s look at aluminum as an example. All the different types of aluminum, such as high-value wrought and lower-value cast alloys that are in our cars, home appliances and other products, are packaged into a recycled material specification known in the industry as “Twitch.” Historically all these mixed alloys were blended together and downcycled, or downgraded, into cast aluminum. This is because there was sufficient demand for cast aluminum. Wrought aluminum producers met their supply through other sources. Over time, the distribution of different types of aluminum alloys that are used in manufacturing has shifted. There’s now a considerable amount of high-value wrought aluminum that’s being lost when it’s downcycled, and wrought producers need more supply to meet growing demand, creating a market for sorting Twitch further into its cast and wrought fractions. This changing market condition was validated at the ReMA National Convention, with the association governance voting to approve a new industry specification called “Vesper,” which is defined as the wrought aluminum sorted from Twitch. There’s now language in place to support buyer and seller agreements, validating the growing demand for sorted products that drive the economics for investing in further processing of mixed scrap metal.
Aly: How does VALIS work with processors to improve their economics and sell inventory domestically?
Emily: At VALIS, we’re building integrated hardware and software solutions that help scrap processors improve the efficiency of their day-to-day operations. We provide them with tools to capture accurate, reliable data on their material quality so they can more effectively monitor their process and sell their products. All that quality data is tied into the digital twin we build of their entire processing line. By integrating with their equipment and capturing production information, we can give them full visibility into the performance of their operations, alert them to issues within their sorting process, and give them tools to predict production volumes based on historical performance. They can tie in pricing metrics to understand the economics of making changes to their operations or help them easily see how improving sortation would contribute to their profitability.
Aly: You’re in market today with VALI-Sample, your sampling product that provides a more efficient way to sample and track composition of drop-out and shredded products. Why have your partners chosen to roll out VALI-Sample across their plants?
Emily: It would be physically impossible to get a detailed analysis of all the metal running through a processing yard. Sampling helps gain visibility into material quality and value, and measure operational performance. Data generated during sampling then informs sales and processing decisions. But today, that data is captured on pen and paper, or analyzed in massive spreadsheets. That leads to human error and a lack of trust in the results. There’s also uncertainty around how well a sample represents reality. Without high quality, reliable data, decision makers are limited in the actions they can take to improve their business. VALI-Sample delivers the accurate data that processors need. It’s an easy-to-use hardware tool that delivers an improved work experience for sampling technicians. It is enabled by a powerful software platform that gives facility managers the ability to audit their sampling process, and sales managers the receipts on material quality they need to back up sales or defend against a claim.
Aly: Like many, I’ve spent more time talking and thinking about tariffs in the past four months than ever before. The metals industry was among the earliest hit––with tariffs on everything from aluminum to copper and steel. How are your customers able to be more agile and resilient to tariffs?
Emily: Tariffs can make it more expensive to import virgin metals for new manufacturing, incentivizing processors to find domestic solutions. Since so many of these metals are partially recovered domestically today, processors who are willing to go the extra mile and do the extra sortation step are going to be much better positioned to supply local smelters and ultimately local manufacturers of new products. By integrating our technology, we can help processors navigate these challenges and capitalize on the opportunities presented by the boom in domestic manufacturing.
Aly: As we close out our discussion, I’ll ask you the question I ask all our founders on “Making Circularity Stick”: What do we need to make circularity stick in the scrap metal industry?
Emily: In a phrase? Cross-value chain collaboration. Looking ahead, we believe that involving the entire ecosystem is key to making circularity the default way of doing things in metals. Automotive manufacturers need to be transparent on alloy specs and source recycled metals, metal producers need to increase recycled content in their systems, scrap processors need to improve the quality of their outputs to better match the requirements of mill processes, and so on. We need all of these actors to work together, challenging what’s possible, and continuously raising the bar on circularity in metals to get there. At VALIS Insights, we are proud to be at the forefront of making circularity stick in the metals recycling industry. By leveraging technology and data, we are partnering with our customers to transform the processing system and pave the way for a more sustainable future together.
“Making Circularity Stick” is a collection of interviews with founders across the Closed Loop Ventures Group portfolio sharing their experiences of making circularity stick across industries. If you’re interested in connecting with the founders sharing their stories, please reach out to Aly Bryan at [email protected].
Disclosure
This publication is for informational purposes only, and nothing contained herein constitutes an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any interest in any investment vehicle managed by Closed Loop Capital Management or any company in which Closed Loop Capital Management or its affiliates have invested. An offer or solicitation will be made only through a final private placement memorandum, subscription agreement and other related documents with respect to a particular investment opportunity and will be subject to the terms and conditions contained in such documents, including the qualifications necessary to become an investor. Closed Loop Capital Management does not utilize its website to provide investment or other advice, and nothing contained herein constitutes a comprehensive or complete statement of the matters discussed or the law relating thereto. Information provided reflects Closed Loop Capital Management’s views as of a particular time and are subject to change without notice. You should obtain relevant and specific professional advice before making any investment decision. Certain information on this Website may contain forward-looking statements, which are subject to risks and uncertainties and speak only as of the date on which they are made. The words “believe”, “expect”, “anticipate”, “optimistic”, “intend”, “aim”, “will” or similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Closed Loop Capital Management undertakes no obligation to update publicly or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise. Past performance is not indicative of future results; no representation is being made that any investment or transaction will or is likely to achieve profits or losses similar to those achieved in the past, or that significant losses will be avoided.
How AI Can Reduce Food Waste at Restaurants
April 11, 2025
Why We Invested in ClearCOGS
Food waste drives significant economic losses to businesses, and the decomposition of organic waste in landfill has become one of the largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions today. According to ReFED, a leading organization focused on tackling food waste across the U.S., over $175 billion worth of food waste (over 17M tons)[1] is generated by consumer-facing businesses, representing an immense opportunity to bring lost value back into our food supply chains.
Today, food waste in consumer-facing businesses is largely caused by operational inefficiencies within foodservice supply chains, such as difficulty forecasting and inefficient preparation techniques, in addition to plate waste. Chain restaurants often overbuy food and over-prep unordered food to avoid missing revenue opportunities. Misaligned production not only results in large volumes of food waste, but also creates major financial losses, given that food costs represent on average 30-50% of a restaurant’s total spend. By improving these operational inefficiencies within this supply chain, food retailers have an opportunity to achieve a net benefit of over $5 billion.[2]
What is needed to improve operations?
Closed Loop Ventures Group––the venture capital arm of Closed Loop Partners, a firm focused on building the circular economy––recently led the seed investment round in ClearCOGS, a leading provider of AI-powered predictive analytics for restaurants, for their platform solution that supports consumer-facing businesses in improving their operations and mitigating food waste.
ClearCOGS offers a comprehensive AI-powered demand planning and data analytics platform for restaurant operators and foodservice businesses, providing exceptional accuracy and immediate benefit to bottom lines. They analyze historical transactions and recipe data provided by the restaurant to generate precise, item-level forecasts that guide prep schedules, ordering and staffing decisions. Their integration with Toast, a leading cloud-based restaurant management software company, offers Toast customers with ClearCOGS accounts a one-click integration for their freemium offerings.
Through their solution, restaurants can make significant improvements to their operations and supply chains, streamlining production and inventory to more accurately meet demand and mitigate the inaccuracies that result in financial and environmental losses.
And the results speak for themselves.
“We were shocked that literally overnight we were able to add 2% to the bottom line with no operational changes.“ Goop Kitchen, Los Angeles, CA
“ClearCOGS reports are more accurate, saving as much as three racks of ribs daily, or more.” Red White & Que, Green Brook, NJ
“Implementing ClearCOGS was an effortless experience. The setup was straightforward, and the team at ClearCOGS provided exceptional support and resources, making it easy to customize the solution to our specific needs.” Blue Square Pizza, Hopkinton, MA
What’s their Special Sauce?
We invested in ClearCOGS knowing that the challenges in restaurants are best understood by those who have worked in them. Matt Wampler, CEO and Co-Founder of ClearCOGS, knows intimately the struggles of running a small business.
At 21, he took on the challenge of turning around a struggling sandwich shop. He put in the hours to successfully turn that around and scale other locations before deciding that helping other owners better manage their own operations was his next challenge. He is perfectly paired with Osa Osarenkhoe, CTO and Co-Founder of ClearCOGS, who studied Electrical Engineering (BA) and Computer Engineering (MA) before working in tech and launching his first start up.
We look forward to seeing what the team will unlock for the restaurant industry, tackling a major source of waste that––when addressed––can result in significant cost savings as valuable materials are diverted from landfill. Closed Loop Partners is delighted to work with ClearCOGS on scaling their solution, preventing food waste at restaurants.
If you are interested in talking more about food waste or getting in touch with ClearCOGS, please reach out.
About Closed Loop Ventures Group at Closed Loop Partners
Closed Loop Partners is at the forefront of building the circular economy. The firm is comprised of three key businesses that create a platform for systems change: an investment group managing venture capital, buyout private equity and catalytic private credit investment strategies, Closed Loop Capital Management; an innovation center, the Center for the Circular Economy; and an operating group, Closed Loop Builders.
The firm’s venture capital strategy, the Closed Loop Ventures Group, has been investing early-stage capital into companies developing breakthrough circular solutions for foundational materials that underpin and significantly influence a wide array of vital sectors of the economy. These materials include organics, minerals, polymers and water. Closed Loop Ventures Group partners with founders and companies who rethink how products are designed, manufactured, consumed and recovered, with the shared vision of reimagining supply chains and eliminating waste. Closed Loop Partners is based in New York City and is a registered B Corp.
To learn about the Closed Loop Ventures Group and apply for funding, visit https://www.closedlooppartners.com/capital-management/apply-for-funding/ventures/
About ClearCOGS
ClearCOGS is an AI-driven forecasting solution designed specifically for restaurant operations. Its predictive analytics simplify critical daily decisions around food prep, ordering, and staffing—helping restaurants reduce food waste, improve operational efficiency, and maximize profitability. To learn more, visit www.clearcogs.com.da
Disclosure
This publication is for informational purposes only, and nothing contained herein constitutes an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any interest in any investment vehicle managed by Closed Loop Capital Management or any company in which Closed Loop Capital Management or its affiliates have invested. An offer or solicitation will be made only through a final private placement memorandum, subscription agreement and other related documents with respect to a particular investment opportunity and will be subject to the terms and conditions contained in such documents, including the qualifications necessary to become an investor. Closed Loop Capital Management does not utilize its website to provide investment or other advice, and nothing contained herein constitutes a comprehensive or complete statement of the matters discussed or the law relating thereto. Information provided reflects Closed Loop Capital Management’s views as of a particular time and are subject to change without notice. You should obtain relevant and specific professional advice before making any investment decision. Certain information on this Website may contain forward-looking statements, which are subject to risks and uncertainties and speak only as of the date on which they are made. The words “believe”, “expect”, “anticipate”, “optimistic”, “intend”, “aim”, “will” or similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Closed Loop Capital Management undertakes no obligation to update publicly or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise. Past performance is not indicative of future results; no representation is being made that any investment or transaction will or is likely to achieve profits or losses similar to those achieved in the past, or that significant losses will be avoided.
[1] ReFed – https://refed.org/food-waste/the-problem
[2] ReFed – https://insights-engine.refed.org/solution-database?dataView=total&indicator=us-dollars-profit&stakeholder=foodservice
Keeping Compost Clean: Tools to Help Reduce Contamination in the Food Waste Stream and Increase Compostable Packaging Recovery
March 17, 2025
This is part of a series of interviews with key players across the composting value chain, conducted by the Composting Consortium, a multi-year industry collaboration managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy. In this series, we spotlight industry initiatives to advance a more robust, resilient composting system that can keep food-contact compostable packaging and food scraps in circulation, to reduce food waste and mitigate climate impact. This week, we are interviewing Eco-Products to learn more about CIRC, an important tool to reduce contamination at composting sites.
Eco-Products®, a Novolex® brand and certified B Corp, is a provider of foodservice packaging made from renewable, recycled and reusable materials. In 2023, the company launched CIRC (Controls Intended to Remove Contamination), an easy-to-use set of customizable tools and frameworks to help generators––such as restaurants and stadiums––packaging manufacturers, distributors, haulers and composters control and manage contamination from non-compostable products and get rid of contamination before it makes its way to the composter.
Composting Consortium: We know that contamination is a systemic challenge and one of the greatest barriers to the recovery of compostable packaging. As a brand who sells and manufactures these compostable materials, tell us how you’re combating the pervasive challenge of contamination in food waste streams.
Eco-Products: Contamination in compost streams is the defining challenge for composters, often leading to inefficiencies and increased costs. We’ve experienced this reality firsthand in Colorado, where Eco-Products is headquartered. Contamination from non-compostable materials has wreaked havoc on the local composting ecosystem in Colorado. We believe that food-contact compostable packaging—in addition to recyclable and reusable materials—has a key role to play in diverting food waste from landfill. We want to see compostable packaging succeed as a solution, but we know that contamination must first be solved to achieve that reality. We know this challenge isn’t exclusive to Colorado, and we knew we had to do something about it, so we developed a program called CIRC (Controls Intended to Remove Contamination).
Composting Consortium: How exactly does the CIRC program work and who is it for?
Eco-Products: Unlike third-party certifications, CIRC is a customizable tool that is designed to build trust, transparency and accountability between generators—such as restaurants, stadiums or event venues—packaging manufacturers, distributors, haulers and composters. The CIRC Toolkit offers a menu of recommended contamination controls spanning Procurement, Operations, Communication, and Composter & Hauler Engagement that we call “the scorecard.” Each section has a list of controls that are practical and useful for mitigating contamination in the compost stream. The program verifies that foodservice operators have taken key steps to avoid sending non-compostable items to composters, ensuring that everyone involved in the composting process is aware of their role in preventing contamination. With CIRC, composters can have greater confidence in the organics streams they receive.
Composting Consortium: Can you give us an example of how a stakeholder can use the tool?
Eco-Products: Yes! For example, a restaurant can reference the ‘Procurement’ section of the scorecard for a list of best practices and guidance when ordering and stocking certified compostable packaging. By following these order requirements, the restaurant can feel confident that the products they’re ordering have been approved by the certifier, the operator and the composter.
Composting Consortium: What makes CIRC different from other solutions?
Eco-Products: One of the standout features of the CIRC program is its open-source nature. This means that anyone, regardless of whether they are an Eco-Products customer, can access and benefit from the program’s resources.
For composters, the primary benefit of CIRC is the reduction in contamination, which leads to more efficient composting processes. With fewer non-compostable materials to sort out, composters can focus on their primary duty: producing high-quality compost.
For haulers and distributors, reducing contamination can lower the costs associated with handling and transporting contaminated loads.
For businesses and organizations committed to food waste reduction, adopting the CIRC program can contribute to a more sustainable waste management system. Restaurants, stadiums, and other venues that implement CIRC can enhance their reputation among environmentally conscious customers. Demonstrating a commitment to reducing waste and supporting composting efforts can attract and retain customers who value sustainability.
Composting Consortium: What advice would you give to brands, generators, haulers or composters who are struggling with contamination?
Eco-Products: Try using CIRC! To date, our program has been piloted at two locations: Knox College in Galesburg, Illinois and the University of Colorado, Boulder. In both instances, we’ve seen great results and dramatically reduced levels of contamination. We are calling on more stakeholders to utilize this free resource and are happy to support any organizations or businesses with the use and implementation of this tool.
Composting Consortium: What are your future plans for the CIRC program and how do you envision supporting the expansion of composting infrastructure?
Eco-Products: We plan to expand our CIRC program this year by creating supplemental resources, including a check list for assessing operational contamination risk factors. By helping reduce contamination issues through CIRC, we aim to help create a pathway for compostable packaging to succeed as a solution for food scrap recovery.
Composting Consortium: What inspired you to join the Composting Consortium as a Material Innovation Partner?
Eco-Products: When we learned that the Composting Consortium launched a Material Innovation Platform last year, we knew we had to get involved. The Composting Consortium’s groundbreaking research and in-market testing over the last three years has paved the way for dialogues in this industry that are helping to move the needle for compostable packaging. In particular, the Disintegration Study was a game-changer for the industry—offering data and proof points on how certified compostable materials break down in compost piles. We’re excited to continue our partnership with the Composting Consortium because we believe that this initiative is uniquely positioned to scale food waste composting infrastructure, help solve for contamination and drive positive, lasting change for the industry.
Why We Invested in Mycocycle: Nature-Inspired Circular Solutions for the Built World
March 05, 2025
The built environment—those man-made structures where we live, work and play—casts a profound impact on our quality of life and well-being. Yet in our current linear “take-make-waste” economy, these same materials bear a tremendous environmental cost, responsible for 39% of global energy related carbon emissions—28% from operational emissions and 11% specifically tied to materials and construction.
Construction and demolition is now one of the biggest sources of waste in the world. By 2025, the annual volume of construction waste generated globally is expected to reach 2.2 billion tons.[1] In the U.S. alone, 600 million tons of construction and demolition debris were generated in 2018, more than twice the amount of municipal solid waste.[2]
The challenge lies not only in sheer volume, but in the complexity of construction materials. Non-concrete waste material––such as wood, drywall, asphalt shingles and tile––often have plasticizers (chemicals that make materials more flexible and easier to mold), trace or heavy metals and polychlorinated compounds in them, making it hard to recover those materials for their next lives. Furthermore, when those materials end up in landfills, they can leach those toxic chemicals into arable land and waterways––where they leave lasting environmental consequences.
Mycocycle, a biotechnology startup, found a solution to help address this complex challenge, inspired by fungi. Their patent-pending process improves the natural functions of fungi to transform construction waste into low-carbon raw materials for the built environment. Within a matter of weeks, their technology can turn organic waste from the built environment––such as carpet fiber and tires––into MycoFIBER©, MycoFILL© and MycoFOAM©, all raw materials that can replace virgin-derived materials.
Closed Loop Partners’ Ventures Group saw a key opportunity in Mycocycle’s technology, a solution that reimagined how materials can be recovered and kept in circulation. This aligned with Closed Loop Ventures Group’s focus on deploying early-stage funding to breakthrough circular solutions for foundational materials that underpin and influence vital sectors of the economy––from water and minerals to polymers and organics. Mycocycle’s solution to recover organic waste in the built environment unlocks new possibilities for circularity across a major industry.
Last year, Closed Loop Ventures Group led Mycocycle’s Series Seed extension to help address the growing challenge of construction waste––with participation from US Venture, the Illinois Department of Commerce and Economic Opportunity INVENT fund, and existing investor TELUS Pollinator Fund for Good.
Since then, over the past 10 months, the Mycocycle team has continued to impress––making significant progress on processing cost reductions and signing exclusivity agreements with major multinational companies for certain product categories. They are demonstrating that not only are their products not harboring the toxic chemicals of their inputs, but they are exhibiting significant performance improvements––in strength, elasticity and more––from the virgin-derived construction products they’re replacing.
Today, the team continues to operate in the south of Chicago––in a space nearly five times the size of the one they were working in over a year ago. And they are filling orders, using mycelium to transform organic waste from the built world into reusable, bio-based ingredients. Those ingredients are going into non-recoverable plastics, replacing food-grade fillers like corn stover, for which higher and better uses exist in biomanufacturing. They are also going into turf applications, replacing materials that have been outlawed in some geographies because of excessive microplastic shedding that pollutes airways and waterways. With products that are both cost competitive against the incumbents and gross margin accretive for the business, Mycocycle is on a path to scale that has already unlocked significant reductions in their processing costs––and there is still room for growth.
A big part of how Closed Loop Ventures Group invests is by identifying founders and leadership teams who balance a “no quitting” attitude with the detail orientation and the project management expertise to move the needle on tough challenges. Joanne Rodriguez, Founder & CEO of Mycocycle, and Colin Litow, COO of Mycocycle, exemplify these characteristics, creating a strong foundation for their team through its next phase of growth.
Today’s reality is that the built environment is still in the early stages of bringing circular principles to bear in the lion’s share of applications. Asynchronous design and demolition processes make it challenging to identify reuse and next life opportunities for materials, and the lifecycle of a building is long enough that it’s rare for an organization to think about disassembly and deconstruction at the time of design. Even if they were, less than 2% of the building stock is new each year.[3] Much more focus is needed on managing renovation and retrofit processes––not just tracking, but on finding new homes for the materials once they’re removed.
Mycocycle is a core part of the solution, as are the companies exploring opportunities to maintain or reduce costs while using recovered materials as inputs into their products. Closed Loop Partners’ Ventures Group is excited to continue to work with the Mycocycle team and those across the manufactured world as they lay the groundwork for a more circular future for the built environment.
About Closed Loop Ventures Group at Closed Loop Partners
Closed Loop Partners is at the forefront of building the circular economy. The firm is comprised of three key businesses that create a platform for systems change: an investment group managing venture capital, buyout private equity and catalytic private credit investment strategies, Closed Loop Capital Management; an innovation center, the Center for the Circular Economy; and an operating group, Closed Loop Builders.
The firm’s venture capital strategy, the Closed Loop Ventures Group, has been investing early-stage capital into companies developing breakthrough circular solutions for foundational materials that underpin and significantly influence a wide array of vital sectors of the economy. These materials include organics, minerals, polymers and water. Closed Loop Ventures Group partners with founders and companies who rethink how products are designed, manufactured, consumed and recovered, with the shared vision of reimagining supply chains and eliminating waste. Closed Loop Partners is based in New York City and is a registered B Corp.
To learn about the Closed Loop Ventures Group and apply for funding, visit www.closedlooppartners.com.
About Mycocycle
Mycocycle, Inc. is a nature-inspired and woman-owned biotechnology startup that leverages fungi to transform industrial waste into reusable materials. Founded in 2018, the company drives circularity in the construction supply chain and diverts waste from landfills. Mycocycle blends lab-cultivated fungi with debris at the point of waste generation to transform waste into new raw materials. To learn more, visit http://www.mycocycle.com.
[1] Source: Construction Dive.
[2] Source: Environmental Protection Agency.
[3] Source: https://www.usgbc.org/articles/existing-buildings-99
Disclosure
This publication is for informational purposes only, and nothing contained herein constitutes an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any interest in any investment vehicle managed by Closed Loop Capital Management or any company in which Closed Loop Capital Management or its affiliates have invested. An offer or solicitation will be made only through a final private placement memorandum, subscription agreement and other related documents with respect to a particular investment opportunity and will be subject to the terms and conditions contained in such documents, including the qualifications necessary to become an investor. Closed Loop Capital Management does not utilize its website to provide investment or other advice, and nothing contained herein constitutes a comprehensive or complete statement of the matters discussed or the law relating thereto. Information provided reflects Closed Loop Capital Management’s views as of a particular time and are subject to change without notice. You should obtain relevant and specific professional advice before making any investment decision. Certain information on this Website may contain forward-looking statements, which are subject to risks and uncertainties and speak only as of the date on which they are made. The words “believe”, “expect”, “anticipate”, “optimistic”, “intend”, “aim”, “will” or similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Closed Loop Capital Management undertakes no obligation to update publicly or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise. Past performance is not indicative of future results; no representation is being made that any investment or transaction will or is likely to achieve profits or losses similar to those achieved in the past, or that significant losses will be avoided.
8 Tips to Navigate Life Cycle Assessments for Circular Packaging
January 29, 2025
Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy highlights the key drivers of greenhouse gas emissions from packaging
Much has been written about why life cycle assessments (LCAs) matter––their role in helping companies choose between different materials and packaging formats, their ability to measure the climate impact of business decisions, even their ability to help evaluate environmental risks of new solutions.
But the reality is, LCAs can become complex very quickly. They usually involve a multitude of assumptions and data––from the origins of materials (cradle) to how they are transported through complicated supply chains, all the way to how they are disposed of (grave) or recovered via reuse or recycling.
Yet if navigated thoughtfully, LCAs are packed with a wealth of information for creating data-backed packaging strategies that contribute to waste reduction goals and advance positive climate impacts.
Here, we share 8 tips to help brands navigate the most critical aspects of any packaging emissions analysis:
- Focus on the biggest drivers of impact: New materials often account for the majority of emissions. Keeping packaging in circulation for longer––thus avoiding the need for new materials––is a key driver to reduce the climate impact of packaging. For reusable containers, the return rate, and the associated number of uses tied to it, is the most critical factor to drive down packaging emissions. When one LCA assumes that a reusable container is used on average 100 times (99% return rate) and another assumes 2 times (50% return rate), emission outcomes will vary widely.
- Put some weight behind the weight of your packaging: Lightweighting is generally the lowest hanging fruit opportunity for companies to reduce their packaging impact. But there’s only so much a product can be lightweighted before this impacts its performance and recyclability. Today, new lightweighting innovations enable durability while not compromising on high packaging quality, functionality and recyclability, opening more opportunities for reduced emissions.
- Account for all distances of transportation, including transport to landfill: In the U.S., virgin materials usually travel hundreds, if not thousands, of miles from production sites to their point of sale. Materials that end up in landfill also travel hundreds of miles from point of consumption to their grave (over 500 miles on average in the case of New York City), but distances traveled to landfill are often overlooked in LCA analyses.
- Give thought to the food waste that packaging may carry to landfills: Food waste in food packaging decays over time and, in the absence of oxygen, creates methane in landfills. Methane, a greenhouse gas, is 28 times more potent than CO2 in trapping atmospheric heat. Any packaging system, such as reusable or compostable options, that serve as a vehicle to properly dispose of (i.e., compost) food scraps, and keep them out of landfills, has significantly reduced emissions compared to current single-use packaging systems.
- Consider the difference between recycling and use of recycled content: The GHG Protocol has two methods for calculating recycling emissions. One method benefits packaging that uses recycled content; the other benefits products that are recycled at end-of-life. Since we need both things to be true to create a truly circular economy, focus on designing packaging that meets both criteria. For LCAs, consider using an average of both calculations.
- Don’t discount impact through incineration: The emissions impact of incineration is left out of many LCAs. In today’s carbon accounting protocols, incineration emissions (i.e., the energy produced from incineration) are accounted for in their next product, thus burning packaging after use does not add to the emissions of that piece of packaging. While this can seem to provide a discount towards packaging emissions, this is not a circular strategy as valuable packaging materials are lost instead of kept in circulation.
- Assess the implication of clean grids: Switching to clean energy is an immediate opportunity to reduce packaging emissions. However, when analyzing the impact of clean grids, remember to apply the benefits of lower manufacturing and transportation emissions to incumbent materials and processes as well.
- Remember that infrastructure assets do not impact emissions directly: Emissions associated with bins, machines and other capital infrastructure are not typically included in packaging LCAs, based on the GHG Protocol. Incumbent solutions like landfilling have infrastructure associated with them as well, and are not included in LCAs, so new infrastructure for future solutions should be held to the same standard as existing infrastructure.
LCAs are just one datapoint within the larger equation
When implementing any packaging solution, emissions are just one part of the equation—packaging decisions affect our planet beyond their climate impact. Waste generated, water usage, biodiversity loss, social and human health risks are all critical aspects to be assessed for a responsible and sustainable circular packaging strategy.
We hope these LCA tips help packaging designers and decision makers make more holistic analyses, leading to greener packaging innovation.
Get in touch with Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy at [email protected] to dive deeper into packaging emissions and to collaborate on designing, testing and scaling circular packaging solutions.
Findings are based on the Center for the Circular Economy’s proprietary LCA model. A special thank you to our partners at Columbia University for their contributions to this work.
The Key to a Strong Local Economy? It Must Be Circular.
January 08, 2025

4 ways the circular economy unlocks local value.
“We are entering the era of the local, circular economy.”
Localization––of industries, supply chains and jobs––is gaining momentum in cities and states across the country. Spurred by increased global trade pressures, pandemic-induced bottlenecks, intensifying climate impacts and increasingly volatile trade routes, a renewed call for local supply chains has emerged.
These appeals have permeated both business and policy: economic regulations increasingly prioritize local goods and production, while ‘Made in America’ initiatives are championed by major corporations like Walmart and Amazon and incentivized by the federal government.
The motivation is clear as the benefits of localization are manifold: when local communities are empowered with ownership of the goods and materials they consume, they reap economic, environmental and social rewards.
For us at Closed Loop Partners, a decade of investing, innovating and building solutions for a waste-free world has taught us the key to a successful local economy: it must be circular.
Lessons from 10 years of local, closed loop initiatives
From its inception, Closed Loop Partners recognized that a circular economy—a system that eliminates waste, recirculates goods and materials, and regenerates nature—goes hand-in-hand with localization.
 Graphic by: Closed Loop Partners
Graphic by: Closed Loop Partners
This vision first came to life when we launched our Closed Loop Infrastructure investment strategy 10 years ago. Leveraging catalytic funding from several of the world’s largest corporations, Closed Loop Partners invested in recycling infrastructure within local municipalities, keeping material out of landfills across the country.
Today, our work has expanded to embody the fullness of circularity, supporting solutions that infuse circularity not only in how we handle waste, but in how we create and maintain goods––through redesigning, remanufacturing, reusing and repairing––with a commitment to localization woven throughout.
“Local supply chains offer smaller, more efficient material loops that avoid leakage, waste and emissions-intensive transportation.”
The more local each stage of production, the more value is shared within local communities, enabling an incentive structure to keep products at their highest and best use for multiple lives.
If we prioritize local circularity and reverse the status quo of long, inefficient and expensive supply chains, the benefits are undeniable.
Here are four outsized impacts that local circularity can unlock:
1) Grow Local Wealth
From designers and engineers to manufacturers and business owners, circularity creates meaningful jobs and economic opportunities in remanufacturing, recommerce, reuse, repair and recycling. It’s estimated that transitioning from today’s linear economy to a circular economy would net 7 to 8 million jobs globally by 2030, many of which are inherently place-based in local manufacturing, repair, reuse and recycling sectors. In the U.S., green jobs are expected to expand to nearly 24 million, comprising 14% of total U.S. jobs by 2030.
In addition to job creation, circularity keeps the value of materials, goods and services in local communities. One such example can be found in our electronics value chain: in lieu of importing raw materials, manufactured electronics and e-waste, a transition to repairing, reselling and disassembling electronics locally keeps valuable metals and minerals within the U.S. production sector. In North America, over 7 metric tons of e-waste are generated per capita––a circular electronics value chain in the region could bring over $8 billion in value back to communities.
One example of a solution to keep more electronics in circulation is Molg, a portfolio company of Closed Loop Partners that’s capturing valuable components and materials from discarded enterprise electronics in Microfactories across the U.S. By disassembling locally, Molg keeps these materials out of landfill while supporting the local economy and job creation—enabling local remanufacturing and resale while reducing the need for imported resources. Molg’s technology is designed to enable cost-effective recovery of components and materials—reducing waste, boosting supply chain resilience and ensuring that valuable resources are recovered for future use.
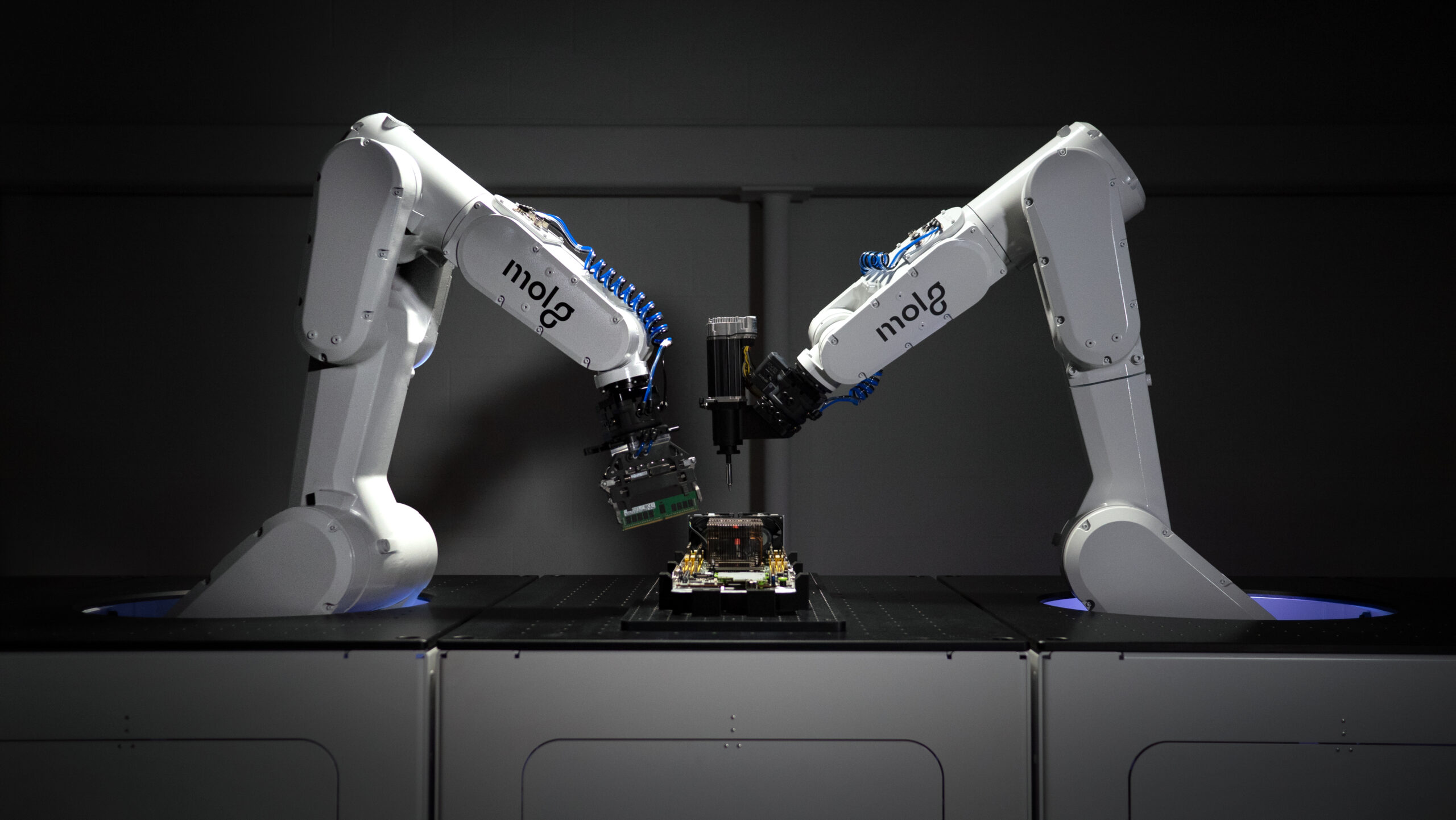 Photo credit: Molg
Photo credit: Molg
2) Reduce Costs (and Emissions)
Beyond value creation, local circularity reduces the economic and environmental costs associated with long, inefficient supply chains. As our economy has globalized, goods and materials traverse an ever-expanding number of transportation nodes that incur unnecessary expenses and emissions.
Consider that 80 percent of the emissions associated with the consumption of goods and services in C40 cities came from goods and services that were imported. To reverse this trend, new circular businesses are working to localize recycling and remanufacturing of critical materials.
One such example is Circular Services, a Closed Loop Partners company and the largest privately held recycling company in the U.S., serving municipalities and commercial properties in some of the nation’s largest and fastest growing cities. Through its network of Circular Resource Facilities, Circular Services collects and processes valuable commodities––including paper, metals, glass, plastics, organics, textiles and electronics––keeping valuable materials in local circulation and improving regional economic and environmental outcomes in the communities in which it operates.
By employing innovative technology within reuse, recycling, remanufacturing and recommerce, resources that were once sent across the country or across the world at end-of-life are now processed locally within Circular Services’ facilities, helping return more materials to supply chains of major consumer brands for continued use at their highest possible value. In 2023, Circular Services put over 1 million tons of materials back into production supply chains, keeping these materials out of landfills, avoiding over 1.6 million metric tons of emissions and saving government and business the cost of landfilling goods.
3) Build Agility (and Resilience)
Long supply chains are inherently rigid and slow to adapt. By shifting towards more local, circular supply chains, we can build shorter, malleable material flows that can more easily respond to changes and disruptions. This also reduces reliance on goods and resources that are located across the world and need to travel long distances through complex supply chains.
With the steady rise of online shopping, the reverse logistics of e-commerce returns is a prime example of a long, complex supply chain rife with silos and inefficiencies. Fillogic, a Closed Loop Partners portfolio company, is reimagining these logistics to bring them closer to home.
 Photo credit: Fillogic
Photo credit: Fillogic
By repurposing under-utilized spaces at shopping malls and strip centers into local logistics hubs, Fillogic activates a network of local retailers and customers, adapting to local needs and conditions. Their technology intercepts unsold garments at the middle mile and redirects them to the appropriate channels for resale. Fillogic provides a complete reverse logistics solution that supports returns, resale, trade in and recycling. By keeping this process local, they avoid sending products through inefficient legacy supply chains—where they traditionally end up as waste—while allowing retailers to adapt to local supply and demand with speed and agility. In 2024 alone, Fillogic kept over 500 million tons of materials in circulation (a 500% increase over 2022), avoiding over 500 million tons of greenhouse gas emissions.
 Photo credit: Fillogic
Photo credit: Fillogic
4) Create Pride
Finally, circularity can foster a sense of pride in local communities. A product that is made and sold locally offers a tangible connection to community and place. A product or service that is remade, resold and that recirculates value locally perpetuates that community connection throughout each of its uses and lifetimes––all while fostering communal responsibility in keeping products out of landfills and the natural environment.
A powerful example of this is the Petaluma Reusable Cup Project in California, led by the NextGen Consortium, an industry collaboration managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy. As a first-of-its-kind initiative, the project made reusable cups the default option in more than 30 restaurants in the City of Petaluma. Consumers were invited to use, return and reuse iconic purple containers in place of disposable, single-use alternatives.
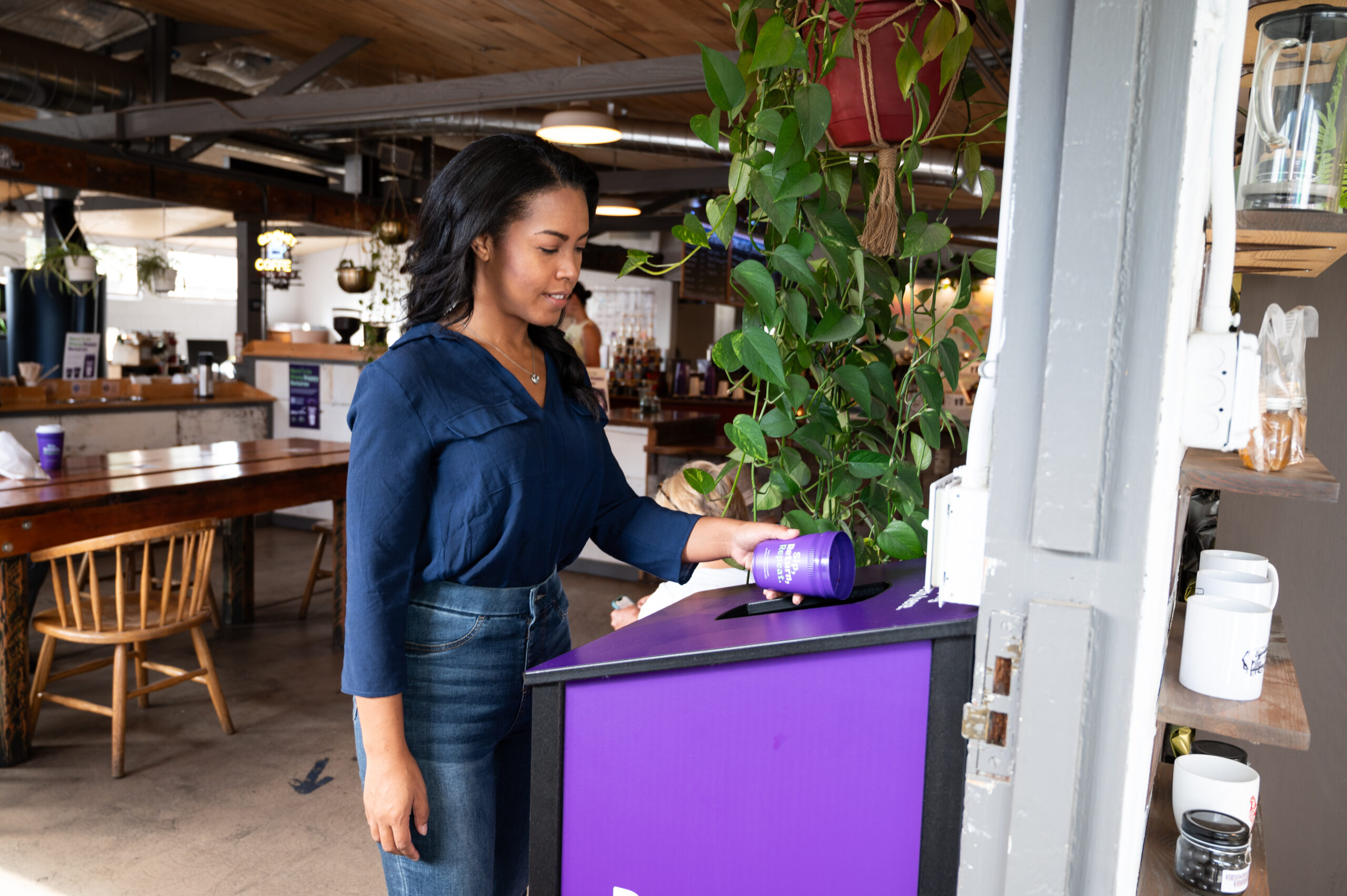 Photo credit: Kellyann Petry
Photo credit: Kellyann Petry
Engaging national brands alongside local establishments and consumers, the project united a network of community members and institutions, inviting shared ownership in reducing local waste, supporting local businesses and maintaining local value. While we are still collecting and analyzing data, the level of community engagement achieved is demonstrated in early findings from the project: over 220,000 cups were returned, ~80% of the Petaluma residents surveyed were aware of the program, and 90%+ of the Petaluma residents surveyed had a very good, good or neutral experience with the program––demonstrating the power of strong, local initiatives.
 Photo credit: Kellyann Petry
Photo credit: Kellyann Petry
Opportunities Ahead
As we reflect on our 10 years of work at Closed Loop Partners, one thing is clear: a resilient, equitable and sustainable economy must be both local and circular––and the solutions to make this possible are on the rise.
To bring this future to life, more investment in local infrastructure, more collaboration across public and private stakeholders, and a renewed focus on capturing the value of materials used to power our economy will be critical. By bringing together localization and material circulation, we can unlock powerful incentives for our communities: increased value, reduced costs, improved agility and pride, to name just a few.
As we look toward an increasingly evolving future––with climate impacts and economic changes, but also with opportunities to rethink the status quo––the importance of this work will only grow. A local circular economy offers a pathway for communities to thrive and adapt to the challenges ahead. It is the key to a prosperous future.
Disclosures
This publication is for informational purposes only, and nothing contained herein constitutes an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any interest in any investment vehicle managed by Closed Loop Capital Management or any company in which Closed Loop Capital Management or its affiliates have invested. An offer or solicitation will be made only through a final private placement memorandum, subscription agreement and other related documents with respect to a particular investment opportunity and will be subject to the terms and conditions contained in such documents, including the qualifications necessary to become an investor. Closed Loop Capital Management does not utilize its website to provide investment or other advice, and nothing contained herein constitutes a comprehensive or complete statement of the matters discussed or the law relating thereto. Information provided reflects Closed Loop Capital Management’s views as of a particular time and are subject to change without notice. You should obtain relevant and specific professional advice before making any investment decision.
Executive endorsements of Closed Loop Capital Management are for illustrative purposes, designed to attract business development contacts, and should not be construed as a client or investor testimonial of Closed Loop Capital Management’s investment advisory services. All such endorsements are from current or former portfolio company leadership about Closed Loop Capital Management’s ability to provide services to their companies. Closed Loop Capital Management has not, directly or indirectly, paid any compensation to such individuals for their endorsements.
The case studies presented in this material have been included as representative transactions to illustrate the platforms, technology and manufacturing capabilities of Closed Loop Partner’s partner companies and are not based on the performance of any investment. The case studies presented in this material are not representative of all Closed Loop Partners’ investments and are not reflective of overall results of any of Closed Loop Partners’ businesses. Not all Closed Loop Partners investments had or will have similar characteristics or experiences as those included herein.
Certain information on this Website may contain forward-looking statements, which are subject to risks and uncertainties and speak only as of the date on which they are made. The words “believe”, “expect”, “anticipate”, “optimistic”, “intend”, “aim”, “will” or similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Closed Loop Capital Management undertakes no obligation to update publicly or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise. Past performance is not indicative of future results; no representation is being made that any investment or transaction will or is likely to achieve profits or losses similar to those achieved in the past, or that significant losses will be avoided.
Why More Composters Are Recovering Food Scraps and Certified Compostable Packaging
January 06, 2025
U.S. composters share on-the-ground insights on how food scraps & compostable packaging collection is improving their business—and offer words of advice to fellow composters. Read insights from Black Earth Compost and Glacial Ridge Composting Facility.
In your own words, tell us about your composting facility and process.
Syed Dong, Black Earth: Black Earth Compost is a curbside compost service for households, businesses, municipalities and schools in Eastern Massachusetts, Rhode Island and New Hampshire, as well as a compost manufacturer. As a site foreman, I operate a hybrid system of aerated static piles and windrows. This is a system of composting that involves forcing air through the piles from pipes underneath then periodically turning piles of compost––also known as windrows. I encourage forced aeration when possible, as it allows for more vector control and has faster processing times than traditional windrow. We accept both food and compostable plastic and fiber products. All materials get tipped inside a receiving building with below grade aeration and blended right away with carbon. After a week or two, it goes onto an above grade pipe system for six weeks then onto curing windrows for two months.
Nathan Reinbold, Glacial Ridge: Glacial Ridge Composting Facility is a regional multi-county composting operation in Minnesota, owned and operated by Pope/Douglas Solid Waste Management. We utilize a covered aerated static pile system designed by Engineered Compost Systems (ECS) to manage the organics stream. We built the facility so that it can be expanded over time to meet a growing need. About 6,500 tons per year of source-separated organics are anticipated to be processed once the composting facility has been fully built out. Partnerships were formed with Pope, Douglas, Grant, Stevens and Otter Tail counties to utilize the facility. Finished compost is sold to landscapers and for youth and civic fundraiser events––called Plate to Garden compost!
Why did you decide to accept food scraps and compostable packaging at your facility?
Black Earth: Accepting both food and compostable products enables us to further address the organics waste crisis that is looming over the nation. Food is a valuable resource that must be recovered, and accepting compostable products helps us recover more of it. By processing both food and compostable products, we can also be a resource to the community by offering material that builds quality soil.
Glacial Ridge: We conduct facility waste composition studies every 5 years as part of our permit process. From this study, we found that a significant portion of our delivered regional multi-county municipal solid waste consisted of food scraps and compostable fiber. We decided to develop an organics collection pilot in 2017, and it has now grown to include a number of regional counties participating with a full-scale commercial composting facility that opened in 2022.
How have you adapted or improved your operations to make food-contact compostable packaging work for your process, while still creating a high-quality finished compost?
Black Earth: There are a lot of great benefits that can be unlocked by accepting compostable products, but more work needs to be done so that non-compostable products don’t also end up in our facility. Currently, machines play a role in controlling the contamination that comes in from conventional plastic products that end up in our facilities because they look like compostable products.* Adding a vacuum has been helpful in combating this issue.
Glacial Ridge: We found that the covered aerated static pile composting process to be very user-friendly for managing the compostable packaging part of the organics stream. All composting facilities in Minnesota adhere to and accept only foodservice packaging that is BPI-certified compostable.** This helps to take the guesswork out of being able to accept compostable packaging and to communicate to customers to only use BPI-certified packaging in order to reduce or eliminate contamination and additional processing costs or processes.
*The Composting Consortium’s research shows that contamination is a challenge for most composters, regardless of their material acceptance policies, business model or size. Moreover, conventional plastic constitutes 85% of the incoming contamination that composters receive—highlighting how important it is to rid look-alikes from the system. For more details, read our report here.
**Glacial Ridge Composting Facility accepts BPI-certified compostable packaging. The Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI) is a leading certification body, alongside other certification bodies in the composting industry, such as the Compost Manufacturing Alliance.
How has accepting food-contact compostable packaging brought value to your business and your community?
Black Earth: So many stakeholders need to be involved and aligned to successfully accept and process certified compostable products that bring value to the composting stream. Since Black Earth Composting is a collection and hauling company, as well as a compost manufacturer, accepting compostable bin liners has made the job of servicing bins easy for our customers and truck drivers. This opens the door to folks that previously saw separating food scraps as messy. Also, this leads to driver retention by making the job a little easier.
Glacial Ridge: Accepting feedstocks, over and beyond only food scraps and napkins, allows Glacial Ridge to be customer and user-friendly. Accepting only BPI-certified compostable packaging allows easier adoption of organics recycling programs and opportunities to divert more food scraps from the waste stream. We also administer a zero waste events program where we connect BPI-compostable packaging and specialized color coded event bins, that are monitored by volunteer/VTO ‘Waste Warriors’, with large scale and community-based events to divert food scraps from the waste stream in a very visible and educational manner to create additional buy-in and acceptance from stakeholders.
Any words of advice to fellow composters who are considering accepting food scraps and compostable packaging?
Black Earth: Don’t be afraid of compostable packaging. Education goes a long way and unlocks new opportunities for the composting business and for broader organics circulation! Start small and educate, educate, educate. While it comes with challenges now, compostable products will continue to play a growing role in replacing single-use conventional plastic and have the potential to replace much of the current contamination we see, and bring in more food to composting facilities. Get ready for it.
Glacial Ridge: I recommend that composters work closely with their state chapter of the USCC. In 2023, the Minnesota Composting Council worked to pass a compostable labeling bill. The purpose of this new law was to reduce misleading product claims, reduce confusion among residents, food establishments and more on what products are accepted for composting. The overarching intention was to reduce contamination at compost facilities resulting in them manufacturing a cleaner, more sellable product. We also recommend utilizing professionally-designed color-coded educational materials to be used on organics carts, dumpsters, roll-offs and inside intermediate collection bins––both public-facing and back of house––that include mention of BPI certification for compostable packaging as the gold standard to reduce confusion and lower contamination concerns.
Scaling Circular Solutions: Why Access to the Right Capital and Partners Matters
December 10, 2024
A case study on the growth of Minus Works, a company invested in by Closed Loop Partners
In the last mile of today’s cold chain, standard single-use plastic encased gel packs are among the biggest sources of waste. With a lack of recovery pathways, the vast majority are discarded in landfill or end up contaminating recycling streams. The challenge lies in what the gel packs are made of: often single-use, non-curbside recyclable low-density polyethylene (LDPE), and a petroleum derivative for the gel.
Yet the growth of industries that are dependent on the cold chain––such as meal kit delivery services––are now facing upcoming Extended Producer Responsibility and “Truth in Labeling” regulations. With these shifts comes an increasing demand for less wasteful alternatives, and a new wave of sustainable cold chain solutions for perishables.
Enter Minus Works, a manufacturing and technology company developing circular solutions to shift the cold chain from linear to circular systems. In 2023, as the Series A startup was building products to reduce waste in the shipping of perishables, clear market demand brought the company to their next phase of growth. But to support this growth and disrupt the cold chain industry, the company required capital and a platform to scale its solution and impact.
Closed Loop Partners’ catalytic private credit group, the Closed Loop Infrastructure Group, having invested heavily in solutions across material collection, sortation, processing, end manufacturing and enabling technology, saw a key opportunity to advance circularity for this industry. Through its platform––an investment firm, innovation center and operating group––Closed Loop Partners is positioned to provide capital, expertise and access to an extensive network spanning entrepreneurs, industry experts, global companies, financial institutions and municipalities. The Closed Loop Infrastructure Group, backed by several of the world’s largest retailers, corporate foundations, industry associations, materials science and consumer goods companies, deployed growth capital––particularly, catalytic debt financing––to accelerate Minus Works’ growth.
Minus Works’ solution aligned with the Infrastructure Group’s mandate. Their alternative gel packs, the BRiQ smarter coolant, used recycled content paper and a compostable gel interior, serving as a non-toxic, circular alternative to single-use plastic wrapped gel packs. By using a recycled fiber casing for their product, Minus Works created a new end market for recycled paper, driving the demand pull-through needed to improve the quality and quantity of materials kept in circulation across North America. Additionally, with freezing co-located at the gel manufacturing site, the company also reduces the required production space by 80%, in turn resulting in lower costs and emissions associated with transportation.
Following its investment, Closed Loop Partners’ Infrastructure Group worked closely with Minus Works, exploring opportunities to refine the product and ensure its circularity at scale. Through its connection to Closed Loop Partners’ larger network, Minus Works was also able to identify alternative financing options for growth that could complement the debt financing they received from Closed Loop Partners.
With funding from Closed Loop Partners and other strategic investors, Minus Works positioned themselves for scale. One year later in October 2024, Minus Works announced their acquisition by Nordic Cold Chain Solutions, a leading provider of cold chain solutions, to further scale their technology and integrate their business within a larger platform of cold chain solutions. This acquisition represents not only a significant milestone in Minus Works’ growth and the important role of catalytic capital––but also signals the inherent value of businesses focusing on circular economy.
As more industries and supply chains demand greater resource efficiency and solutions that reduce waste and emissions, circular economy infrastructure and technologies will be pivotal. Catalytic capital will continue to play an important role in the growth of circular economy solutions. Its ability to accelerate and de-risk the development of high-impact projects and companies opens opportunities to attract additional forms of traditional financing that can bolster growth.
Closed Loop Partners’ Infrastructure Group, building on Closed Loop Partners’ 10-year track record, continues to deploy a flexible mix of financing solutions––such as secured and unsecured loans and mezzanine debt, or catalytic equity financing––supporting companies, cities and projects that need access to large pools of capital. Through a platform of support, we aim to transform industries, keep more materials in circulation and accelerate the transition to a circular economy.
To learn more about Closed Loop Partners’ Infrastructure Group and apply for funding, visit here.
Disclosure
This publication is for informational purposes only, and nothing contained herein constitutes an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any interest in any investment vehicle managed by Closed Loop Capital Management or any company in which Closed Loop Capital Management or its affiliates have invested. An offer or solicitation will be made only through a final private placement memorandum, subscription agreement and other related documents with respect to a particular investment opportunity and will be subject to the terms and conditions contained in such documents, including the qualifications necessary to become an investor. Closed Loop Capital Management does not utilize its website to provide investment or other advice, and nothing contained herein constitutes a comprehensive or complete statement of the matters discussed or the law relating thereto. Information provided reflects Closed Loop Capital Management’s views as of a particular time and are subject to change without notice. You should obtain relevant and specific professional advice before making any investment decision.
Executive endorsements of Closed Loop Capital Management are for illustrative purposes, designed to attract business development contacts, and should not be construed as a client or investor testimonial of Closed Loop Capital Management’s investment advisory services. All such endorsements are from current or former portfolio company leadership about Closed Loop Capital Management’s ability to provide services to their companies. Closed Loop Capital Management has not, directly or indirectly, paid any compensation to such individuals for their endorsements.
The Case Studies described on the Website are included as representative transactions to demonstrate assets to which Closed Loop Capital Management provides capital, however, are not representative of all Closed Loop Capital Management investments and are not necessarily reflective of overall results of any of Closed Loop Capital Management’s businesses. Investments in other businesses may have materially different results. Not all Closed Loop Capital Management investments had or will have similar characteristics or experiences as those included herein.
Certain information on this Website may contain forward-looking statements, which are subject to risks and uncertainties and speak only as of the date on which they are made. The words “believe”, “expect”, “anticipate”, “optimistic”, “intend”, “aim”, “will” or similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Closed Loop Capital Management undertakes no obligation to update publicly or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise. Past performance is not indicative of future results; no representation is being made that any investment or transaction will or is likely to achieve profits or losses similar to those achieved in the past, or that significant losses will be avoided.
Making Circularity Stick: Electronics
November 21, 2024
A conversation with Rob Lawson-Shanks, CEO of Molg & Aly Bryan of Closed Loop Ventures Group
Advancing electronics circularity has long been a core part of our investment focus at Closed Loop Partners. That has only accelerated as state and federal governments have increased focus on domestic manufacturing for electronics, right-to-repair laws and domestic sourcing of metals and minerals needed for the energy transition.
For servers specifically, we’re caught in between accelerated market growth and simultaneous accelerated obsolescence of these devices. An 8.3% compound annual growth rate is expected to result in a market size of $230B by 2034––at the same time, more existing technology continues to fall obsolete with generative AI dramatically driving up computing needs. With nearly 14 billion servers shipped in 2023, and the average life expectancy of a server down to three to four years, processing and repurposing these assets for their next life in lower computational applications is critical.
In the discussion that follows, Rob Lawson-Shanks, Co-founder and CEO of Closed Loop Ventures Group portfolio company Molg, speaks with Aly Bryan, Investor on the Closed Loop Ventures team at Closed Loop Partners, about how Molg is supporting hyper-scalers––large-scale data centers that provide cloud computing and storage services to organizations and individuals––and their partners to improve recovery and utilization of these assets, ultimately making circularity stick in the electronics industry.
Rob: My name is Rob Lawson-Shanks and I’m the Co-founder and CEO of Molg.
Aly: And I’m Aly Bryan, an investor on the Closed Loop Ventures team at Closed Loop Partners. I also have the distinct pleasure of serving on Molg’s Board of Directors. Rob, can you please start us off by sharing a bit about what you’re building at Molg?
Rob: At Molg, we support hyper-scalers, electronics manufacturers and their partners in advancing a circular economy for electronics––focusing today on servers and laptops, two key devices with increasing opportunity to recover materials at scale.
Aly: Why do you think circular economy is important to your partners?
Rob: Our customers are experiencing tremendous demand for computing ability––resulting in significant growth of their existing data center footprints. In many cases, our partners are growing so fast that they’re outpacing the supply of the very materials they need to bring new assets online. Molg helps our partners recover and reuse legacy assets––like CPUs, memory cards and more––that otherwise would need to be purchased new, helping to get new data centers online faster and saving hyper-scalers money in the process.
Aly: Today, Rob and I will explore how to identify strong partners and then work with them to scale, where grant dollars can help to support growth of the business, and ultimately tackle how he thinks we can make circularity stick in the electronics industry. Let’s get started!
On Identifying Strong Partners
Aly: Molg has a partnership with Sims Lifecycle Services as well as other hyper-scalers, and you have worked with Dell and other consumer electronics companies in the past few years. How did you go about identifying the right partners within each of those organizations? What makes them strong partners for you as you look to scale?
Rob: When identifying the right partners, we look for alignment in three key areas: shared mission, complementary capabilities and a commitment to innovation. For us, it’s not just about who can provide access to assets or resources but who is genuinely invested in advancing the circular economy.
Take Sims Lifecycle Services, for example. They’re at the forefront of electronics recycling and resource recovery. Their deep expertise and established infrastructure are critical for closing the loop on materials. It’s this operational strength that makes them an ideal partner for us to deploy our Microfactories with. They bring the logistical muscle, and we bring the cutting-edge technology to recover and repurpose high-value components efficiently, creating a seamless integration that amplifies impact.
On Sources of Funding
Aly: I’ve always been impressed with the way your team has balanced commercial arrangements with government funding, including your recently announced $5 million grant from the Department of Energy. How do you think about the role of grant dollars in supporting the growth of the business?
Rob: We’re in a once-in-a-generation moment where the government is investing unprecedented funding into reshaping industrial policy, bringing supply chains back to the U.S., and creating powerful opportunities for resilience and circularity in the process.
This $5 million grant directly accelerates our ability to scale our Microfactory technology, allowing us to create meaningful contributions to circularity at a much faster pace.
What’s even more exciting is that this project is being executed in partnership with several of our commercial partners, which means the impact of the Department of Energy’s investment is amplified through real-world deployments. It’s a collaborative approach that not only validates our technology but also sets the foundation for a more sustainable and resilient electronics supply chain in the U.S.
Aly: Earlier this year, you closed a $5.5 million Series Seed with participation from Amazon Climate Pledge Fund, ABB Ventures, Overture VC, Elemental Impact and of course us at Closed Loop Partners. What will this new capital help unlock for the business?
Rob: First, I want to extend a huge thank you to Closed Loop Partners’ Ventures Group for leading our Series Seed round and for your continued support. It’s been instrumental in getting us to this point. The funding from you and our incredible partners allows us to meet the rapidly growing demand from our customers who are increasingly prioritizing circularity.
The need for circular solutions is accelerating at an incredible pace, and the scale of the problem requires companies like ours to grow quickly to support this demand. For us, it was crucial to have backing from mission-aligned partners like Closed Loop Partners, who see not only the massive financial opportunity but also the transformative potential for creating circular supply chains.
On Commercial Contracts
Aly: I’d be remiss not to ask on behalf of all the other circular economy founders out there working to get their first commercial contracts over the line. What advice would you have for those founders on how to most effectively navigate those conversations?
Rob: These commercial partnerships are absolutely critical because the biggest impact on circularity comes from working with large companies that operate at a significant scale. To make meaningful change, you need to engage with Fortune 100 and 500 companies where your solutions can have the most transformative effect.
One piece of advice I would offer is to truly understand the mission and values of your potential partners. Early on, I found it invaluable to dig into their ESG reports and public statements to see what they’re prioritizing and where your solutions can align. It’s about finding that overlap between your goals and theirs, which often forms the basis of a strong partnership.
It’s also important to recognize that circularity is challenging and it’s a journey—there’s no single solution that will instantly make a company circular. It takes patience, empathy and an iterative approach. You have to be willing to work closely with your partners, especially understanding that it’s a give-and-take process as you incrementally build towards the larger, more holistic systems we all envision.
For me, it’s always been about approaching these contracts from a partnership mindset. Instead of just selling a product, focus on how you can co-create value and support each other through the inevitable challenges. That collaborative spirit is what will drive real progress and help you navigate those early conversations effectively.
On Making Circularity Stick
Aly: Last question! How can we make circularity stick in the electronics industry?
Rob: Well, first off, we could start by making things less sticky by not using glue and adhesives in electronic design! But on a more serious note, it’s really about forming strong partnerships across the entire ecosystem and pushing each other in our respective roles to make circularity the default way of doing things. We need manufacturers, users, recovery partners and second-life users all working together, challenging what’s possible, and continuously raising the bar on circularity until it’s just how we operate as an industry.
“Making Circularity Stick” is a collection of interviews with founders across the Closed Loop Ventures Group portfolio sharing their experiences of making circularity stick across industries. If you’re interested in connecting with the founders sharing their stories, please reach out to Aly Bryan at [email protected].
Disclosure
This publication is for informational purposes only, and nothing contained herein constitutes an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any interest in any investment vehicle managed by Closed Loop Capital Management or any company in which Closed Loop Capital Management or its affiliates have invested. An offer or solicitation will be made only through a final private placement memorandum, subscription agreement and other related documents with respect to a particular investment opportunity and will be subject to the terms and conditions contained in such documents, including the qualifications necessary to become an investor. Closed Loop Capital Management does not utilize its website to provide investment or other advice, and nothing contained herein constitutes a comprehensive or complete statement of the matters discussed or the law relating thereto. Information provided reflects Closed Loop Capital Management’s views as of a particular time and are subject to change without notice. You should obtain relevant and specific professional advice before making any investment decision.
Executive endorsements of Closed Loop Capital Management are for illustrative purposes, designed to attract business development contacts, and should not be construed as a client or investor testimonial of Closed Loop Capital Management’s investment advisory services. All such endorsements are from current or former portfolio company leadership about Closed Loop Capital Management’s ability to provide services to their companies. Closed Loop Capital Management has not, directly or indirectly, paid any compensation to such individuals for their endorsements.
The Case Studies described on the Website are included as representative transactions to demonstrate assets to which Closed Loop Capital Management provides capital, however, are not representative of all Closed Loop Capital Management investments and are not necessarily reflective of overall results of any of Closed Loop Capital Management’s businesses. Investments in other businesses may have materially different results. Not all Closed Loop Capital Management investments had or will have similar characteristics or experiences as those included herein.
Certain information on this Website may contain forward-looking statements, which are subject to risks and uncertainties and speak only as of the date on which they are made. The words “believe”, “expect”, “anticipate”, “optimistic”, “intend”, “aim”, “will” or similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Closed Loop Capital Management undertakes no obligation to update publicly or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise. Past performance is not indicative of future results; no representation is being made that any investment or transaction will or is likely to achieve profits or losses similar to those achieved in the past, or that significant losses will be avoided.
Does Compostable Packaging Actually Turn into Compost? Industry Experts Share Insights
October 31, 2024
Compostable packaging has become increasingly popular on retail shelves––but can it turn into compost if accepted at composting facilities?
In a joint interview, field testing experts, including the Compost Manufacturing Alliance and the Compostable Field Testing Program—both partners of the Composting Consortium, an industry collaboration managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy—share what they have uncovered after 10+ years of in-field experience.
Read more to find out how well compostable packaging actually breaks down into compost, and what’s needed for these materials to work in the organics stream. Curious to learn more about how field testing works? Scroll to the bottom of this post to learn more.
What is your organization’s role in the composting industry?
Compost Manufacturing Alliance (CMA): CMA field tests compostable packaging disintegration and reviews acceptance criteria for some of the largest composting facilities in the U.S. and Canada. Our published list of certified and accepted compostable products includes a significant percentage of compostables throughout North America, with over 5,000 unique, individual products certified or approved from hundreds of global manufacturers. CMA originated from composter-led efforts to address the challenge of some certified compostable packaging not breaking down in the compost process. In 2007, Cedar Grove started a field testing program to develop lists of accepted compostables for its municipal partners and commercial clients, which became nationally recognized. In 2016, CMA’s founder, Susan Thoman, expanded Cedar Grove’s program nationwide, partnering with five large compost facilities. Today, CMA aims to ensure compostable packaging disintegrates properly, protecting composter and packaging manufacturers’ investments and preventing landfill waste.
Compostable Field Testing Program (CFTP): CFTP supports composters with methods and test kits to field test compostable product disintegration at their sites. We then collect and open source the resulting data, including both product disintegration and compost operating conditions. As an international, nonprofit research platform, we look to understand how compostable products break down in real-world conditions. Founded in 2016 by the Compost Research & Education Foundation and BSIbio, our origins begin in 2013 working with university partners to refine and pilot the US Composting Council’s (USCC’s) original “mesh bag” field test method and create a new “dose” method for sites where a bag won’t work.
Composting Consortium (CC): The Composting Consortium, managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy, conducts in-market tests and in-depth research to support the industry in advancing composting infrastructure and the recovery and processing of food-contact compostable packaging and food scraps in the U.S. We launched in 2021, bringing together leading voices across the composting and compostable packaging value chain––from the world’s leading brands to best-in-class composters running the operations on the ground.
Why is field testing compostable packaging important?
CFTP: Composters can only accept compostable packaging if they know that these materials will truly break down and not negatively impact their end product––healthy compost! Biodegradation testing, which happens in a lab environment, is important. It proves that an item is really getting converted at a molecular level by microbial activity. But disintegration testing to see compostable products visibly breaking down is equally important. Field testing compostable packaging is a way to bridge between lab results and real-world disintegration in actual industrial and commercial settings.
CMA: It’s critical to building trust in the composting industry. Many of today’s largest facilities must use technology that works for an evolving list of feedstocks, including post-consumer food scraps. These are different systems than what was used in the beginning years of yard waste and pre-consumer food scrap composting. Commercial composting and compostable packaging have evolved significantly and are continually improving. It’s true that lab standards are now only one step in confirming product safety and disintegration in various composting systems. Products must be proven to break down in facilities to ensure they are not treated as contaminants and end up in landfills.
CC: Compostable packaging is a promising innovation for diverting food waste from landfills to composting facilities, but to be successful, infrastructure must be willing and able to process these materials. Prior to 2024, limited public information existed on the performance of compostable packaging, and we’re glad to see that is changing. Data from field testing replaces anecdotes with data that can drive discussions, decisions and policymaking that will shape a more resilient future for the composting and compostable packaging industries.
What are some of your key findings thus far?
CMA: Contrary to common belief, biopolymers generally disintegrate well in composting. Fiber-based products do not disintegrate as well as biopolymers overall, although compost manufacturers are more comfortable taking in fibers because bioplastics often resemble traditional plastics and are often sorted into the organics bin by mistake. We are also narrowing down the composting conditions that most affect product disintegration. While time is certainly a factor, it is not necessarily conclusive. The interaction between time, moisture, carbon to nitrogen ratio and agitation is complex and dynamic. Our data suggests that no single variable can be considered the key to successfully breaking down compostable products. Each variable within this set of acceptable conditions––such as moisture, carbon to nitrogen, bulk density––affects other variables.
CC: Our report features our top 10 findings, and to be even more succinct, we can boil it down to three key takeaways. First, certified food-contact compostable packaging breaks down effectively at commercial composting facilities that meet reasonable operating parameters––such as moisture, water and temperature––as defined by the Composting Handbook. We collaborated with composters to collect daily and weekly pile readings within these parameters. Second, compostable plastic and fiber packaging met field-testing thresholds for disintegration, achieving 80% and 90% thresholds at the material category level, as per CMA’s standards. Lastly, fiber packaging disintegration improves with mechanical or manual agitation and consistent moisture levels above 50%. For more details, read our report here.
CFTP: Our data shows us that composter acceptance is more complex than just whether a material will disintegrate or not––contamination mitigation, and the role of materials in the composting process play an important part. The results for fiber products always surprise folks; both lined and unlined fiber products––such as “food-soiled paper”––don’t tend to break down as quickly as we might expect, despite their widespread acceptance. On the other hand, biopolymers consistently prove to break down better than what is anecdotally reported in the field. In either case, tests across different technologies––like windrow and aerated static pile––have shown that the operating conditions have to be right for the products to break down. Temperature and moisture have the most significant impacts. The right conditions vary by material, and these conditions apply regardless of technology. Our new online Results Dashboard allows visitors to view how different materials perform, in different facility types and under different conditions.
Where have you seen opportunities for further collaboration or joint work?
CMA: Research in this space is vitally important, but funding for research is scant. Pooling resources to fund, design and conduct research can move the composting and compostable products industries forward faster and more efficiently than any one entity can alone. Conversations, like this one, can shed light on different stakeholders’ perspectives and where we can find common ground. From that common ground, we can each use our own platforms to dispel misperceptions that often lead to bad policy and thwart true progress.
CFTP: Although disintegration trends appear similar across data sets, there are tangible differences in methodology between different testing groups that could benefit from standardization. Creating a collaborative industry standard for field testing could result in more reliable testing and more comparable data between tests. We’ve been collaborating to standardize methods since 2021 under ASTM International, one body which published lab-based disintegration and compostability testing and labeling standards in the 1990s.
CC: Given the key insights that are similar across our organizations, working together to educate composters, policymakers, and packaging manufacturers and brands on the topic of field testing can help expand end-of-life options for compostable materials and close the loop on food waste. We’re really proud of the way our teams are collaborating already! We are all contributing to the development of an ASTM field testing standard, and our team will donate data to developing this method, like we have to CFTP for the launch of its open-source database.
Any final thoughts?
CFTP: Compost operations are as unique as fingerprints, and even a single composter using the same technology will experience a range of operating conditions––such as temperature and moisture––season-to-season or pile-to-pile. Pursuing research on field testing results that correlate to operating conditions is going to help move the needle on understanding compostable packaging, and help composters feel confident in accepting these products, without having to test every product themselves. Importantly, field testing alone can’t solve the challenges facing the circular economy for food scraps and compostable packaging. An aligned and science-based approach that ties policy, systems and technology together is essential, and it’s for this that the CFTP’s non-profit and open-source approach is designed.
CMA: CMA continues to hold a space to connect product designers with compost manufacturers. When we collectively work manufacturer-to-manufacturer, we have a much more efficient way to address the disintegration performance of materials in real world systems. Working together, we can explore the relationship between product constituencies and pile science. Continued collaboration around field disintegration testing and settling on a method, and then a standard, within the ASTM D34 committee, can harmonize research efforts and provide all stakeholders with greater clarity and focus for the future.
CC: Our team has launched several new programs to engage packaging manufacturers, composters and municipalities (cities and counties) to scale infrastructure, and we welcome a conversation with these groups about the results of our disintegration study. If you want to learn more about how we’re supporting the scale up of composting infrastructure, please reach out to Caroline Barry at [email protected].
Learn more about how field testing works below!
How do you test the disintegration of certified compostable packaging?
CMA: The “mesh bag” method has been central to CMA’s composter-centered testing for nearly 20 years. Samples are marked, placed in mesh bags, and layered within a freshly made compost pile at a commercial facility. What makes our testing distinct is that CMA retrieves the mesh bags at the end of the active cycle, as opposed to the end of the curing phase. This means that the bags are extracted, cooled and dried, then our field technicians sift each bag and samples are sent to the lab for further processing. CMA evaluates visual disintegration, which aligns to compost manufacturers’ concerns about visual contamination in their end-product. Our thresholds to “pass” CMA’s field-testing criteria for certification are based on composters’ perspectives. Fiber-based remnants in finished compost are generally considered less problematic than plastic remnants because fiber-based remnants will often continue to disintegrate after active composting, just as they do in ambient conditions. Compostable biopolymers, on the other hand, may or may not continue to disintegrate after active composting and can look like conventional plastic in the finished product. Thus, compostable biopolymers must show >90% disintegration to pass while fiber-based products must show >80% disintegration.
CC: Our disintegration study tested over 23,000 units of fiber and compostable plastic packaging, making it the largest field test of certified compostable packaging in North America. All products and packaging tested in our pilot were either BPI-certified or in the process of certification. This intentional choice ensured no harmful chemicals, such as PFAS, were deliberately introduced into the composting process. We trialed both the mesh bag method and the dose method. Disintegration was measured by percentage reduction in weight and surface area at Day ~47 and at the end of the curing phase. The compostable packaging remained in the compost piles for 49 to 94 days, depending on the facility’s technology. A distinct aspect of our study is the level of data and detail we’ve obtained on composting parameters––such as temperature, moisture and more––alongside disintegration results, which were assessed both in-field and in-lab. Compost operators tracked daily pile temperature, weekly moisture and oxygen readings, and periodically measured bulk density, pH, carbon to nitrogen ratios, compost maturity, and stability. This comprehensive data collection allowed us to correlate the composting conditions with the disintegration performance of the packaging, providing valuable insights into the effectiveness of different composting processes.
CFTP: Most field tests we’ve coordinated have used the ‘mesh bag’ method, where several different items are packed with compost feedstock into a large mesh bag. The bag is tracked along with operating conditions like temperature, moisture and compost maturity, throughout the full composting process, both active composting and curing. At the end of the test, the material in the bag is sifted. Residuals from the test items are extracted and analyzed to measure disintegration by both weight and surface area. We provide a baseline test kit with the same test items across all tests, so we can better see the impact operating conditions have on disintegration. We also developed the “dose” method, similar to the mesh bag method, but with test items loosely piled instead of bagged. More details are available on the CFTP’s results dashboard and website as of fall 2024!
How do your approaches to field testing align or differ from the other groups here? What should stakeholders understand about the differences and similarities in your approaches?
CMA: Cedar Grove Composting’s initial method has been widely adopted, leading to similar mesh bag techniques across organizations. However, CMA has refined its approach, using Ingeo™ PLA as the primary control due to its consistent disintegration in all composting processes. Office paper is also used, though its disintegration varies. CMA avoids the “bulk dose” or open pile method, which places samples directly into the pile. Despite logistical challenges, this method may evolve with continued use. CMA tests products in “real world” scenarios with no pre-shredding or pre-treatment of samples, and only tests disintegration during the active composting phase, unlike other tests that extend into the curing phase, and/or may use pre-shredded or pre-treated samples. Certification requires evaluation after the active phase because some composters screen materials between these phases. Products without additional curing are screened out and reprocessed or sent to the landfill. CMA extends studies through the curing phase upon request but bases certification on active phase results to align with typical composting practices.
CFTP: As a non-profit project, the Compostable Field Testing Program’s activities are funded by grants and donations, both financial and in-kind. The CFTP is committed to open-sourcing the data it collects in as much detail as possible, while honoring our commitment to anonymizing facility’s operating data. CFTP is rooted in collaboration between organizations supporting the circular economy and science-based research to advance industry and inform policy, evidenced by our founding partners BSIbio and CREF, and in providing advisory and implementation services for the Composting Consortium’s Disintegration Study. This model has kept the program grounded in science and problem solving, supported by forward thinking organizations. Also, relative to other field testing initiatives which tend to focus on larger–scale facilities, the CFTP aims to make field testing accessible to composters of all sizes, from community-scale to the largest commercial-scale facilities.
CC: Since our start, the Consortium has aimed to be additive in the field of compostable packaging testing, collaborating with several of our partners including CMA, CFTP and CREF along the way. We were the first group to trial the still-developing ASTM field testing method, where both CFTP and CMA participate. We have donated data to CFTP to support the public launch of their open-source database, and we belong to international collaborations to share insights about our experience field testing compostables. One key difference in our approach is that we measured disintegration at 2 points of the compost process (Day 47 and at the end of curing). This means we may have pulled the mesh bags or packaging from the compost piles later than other field testing groups. We also did not test packaging with the intention of passing or failing any one product. We’ve collected as much data as we have with the intention of applying it to support best management practices for composers who want to accept these materials. While we will not carry out more field tests in the next two years—CMA and CFTP have that covered—we intend to work with the USCC to integrate our findings to update best management practices for composters who accept these materials.
