In 2018, the NextGen Consortium launched its first initiative, the NextGen Cup Challenge––a global design competition seeking to identify and commercialize existing and future solutions for the single-use, hot and cold fiber cup system. Students, manufacturers, entrepreneurs, designers and businesses were invited to submit their ideas for the cup of the future. After a rigorous four-month review process, the Challenge narrowed nearly 500 submissions from over 50 countries down to 12 winners.
These 12 winning solutions––broadly categorized into innovative cup liners, new materials and reusable cup service models––were chosen for their potential to help turn the 250 billion fiber to-go cups used annually from waste into valuable materials that can be reused and recovered.
Today, many of these innovations continue to disrupt the status quo of the single-use cup, a seemingly convenient product that has come with a steep price over the years: cups ending up in landfills, creating greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change. As companies look for ways to shift their business practices away from a wasteful take-make-waste system, there are tremendous opportunities for new solutions. The next wave of cup design is more innovative than ever, with new materials that can reduce environmental impact, and new systems that can keep valuable materials in play for longer.
Over the last three years, we’ve seen the pandemic alter consumer preferences, more corporations commit to sustainability goals, and policy transform the landscape for circular packaging solutions, including reuse models. Amidst all these changes, NextGen Cup Challenge winners are paving a path forward in line with four key trends:
1. New materials are increasingly competitive as an alternative to single-use plastic

NextGen Cup Challenge winner, Footprint, continues to expand in its mission to replace single-use plastics with plant-based fiber at major food companies, retailers and consumer packaged goods companies, across categories including shelf-stable cups, meat trays and dairy. The company’s plant-based plates, bowls and other food-service items are in concession stands at Footprint Center, home of the winning NBA and WNBA teams, Phoenix Suns and Phoenix Mercury. This long-term naming-rights partnership between Footprint and the Suns management group puts a spotlight on sustainability, fan education and reducing the environmental impact of sports and entertainment events. In December 2021, Footprint announced a SPAC merger with Gores Holdings VIII, and is accelerating growth in key verticals like supermarkets, stadiums, and geographically in Europe, opening an R&D center in Eindhoven, The Netherlands, and expanding production in Poland with new factories coming online in the coming year.

NextGen Cup Challenge winner, MM Kotkamills Boards, is developing new materials for a range of packaging types, including and beyond the cup. The company’s Oy’s ISLA® Duo material for hot beverages offers an alternative to polyethylene (PE) extrusion-based cups. The product is now in regular production and sold worldwide. MM Kotkamills has also widened their family of sustainable barrier board products with their new ISLA® Ice and Cream board solution for selling ice cream in retail stores and over the counter. Their new generation fiber solution-based ISLA® Duo is widely used in the event industry. The fiber-based cups are collected and recycled, with the cups’ wood fibers reused in the production of other fiber-based sustainable solutions, such as tissue paper or corrugated board.

Colombier has widened their product range since winning the NextGen Cup Challenge. Their EcoBarrier Flex™, a pure paper solution with an innovative barrier, acts like plastic to preserve food products, prolonging shelf-life. EcoBarrier Flex was designed as primary packaging for cookies, potato chips, candy, food bars, powders and other food products, and is now piloting with major food brands.
2. Reuse is going mainstream
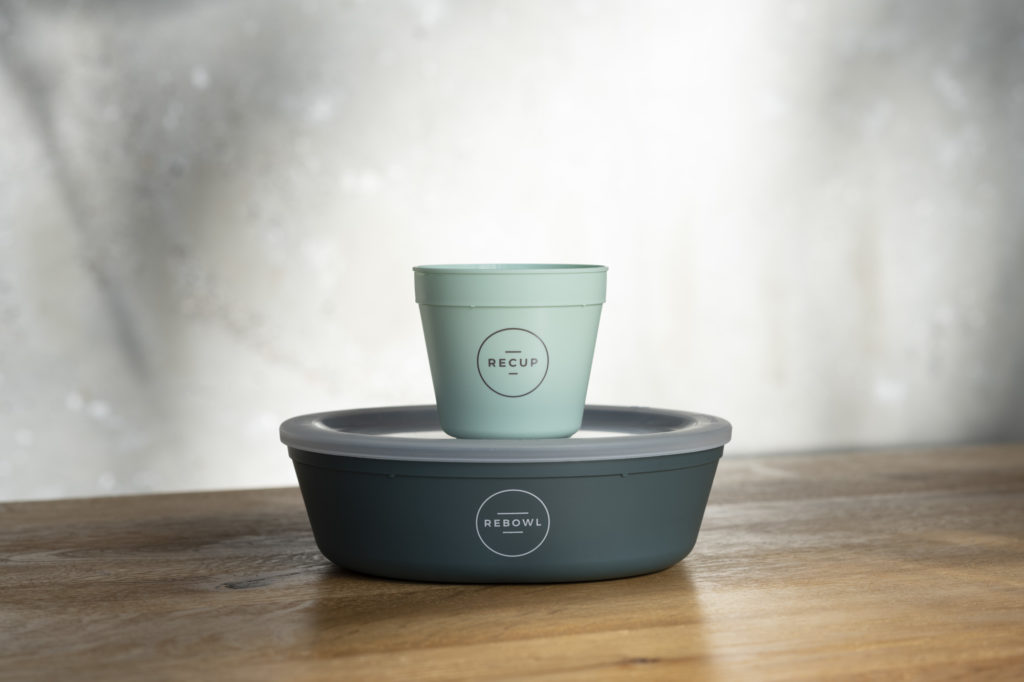

Significant changes have happened in its home country of Germany since RECUP was announced as one of the winners of the NextGen Cup Challenge. A law was passed that obliges catering establishments to offer a reusable alternative for to-go food packaging, advancing more widespread use of reusable systems. This important milestone supports the continued growth of RECUP, especially as they launch REBOWL, their new reusable alternative for take-away food. Since the NextGen Cup Challenge, RECUP has received several honors for their reusable packaging, including the “Blauer Engel”, the “European Reusable Award” and the Bavarian Environmental Medal. In 2020, RECUP partnered with McDonald’s in Germany on a reusable cup system.
3. Strategic partnerships are expanding the reach of innovative solutions
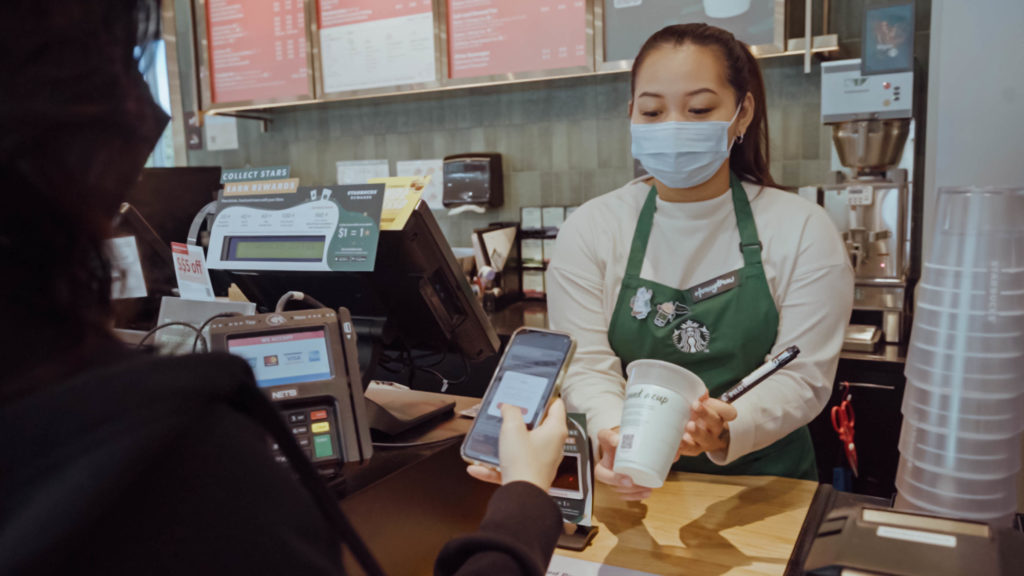

Since winning the NextGen Cup Challenge, Muuse has grown its network around the world. In 2019, the company expanded their track and trace reuse service in Hong Kong and partnered with Swire Properties to reduce waste within Taikoo Place. In 2021, they expanded their reuse service in Toronto, Canada. And in early 2022, they launched a partnership with Starbucks, enabling reuse at Starbucks stores at the National University of Singapore. They have also been working with GrabFood and food panda in Singapore to provide reusables for food delivery. Overall, they have been able to save 70,000+ single-use items from entering the waste stream, working with over 100 partners. In 2021, the team lost their founder, Brian Reilly, who is greatly missed by his family, friends, and colleagues. The Muuse team is extremely honored to continue out his legacy and push forward his vision for reuse.
NextGen Cup Challenge winner WestRock recently joined forces with Tim Hortons as a brand partner for their pilot cup, which is expected to launch soon at select Vancouver restaurants. In addition to innovating a recyclable cup, the company continues to explore recyclable barrier technologies designed for the specific needs of other food packaging, including ice cream pints, lined water cups and yogurt cups.
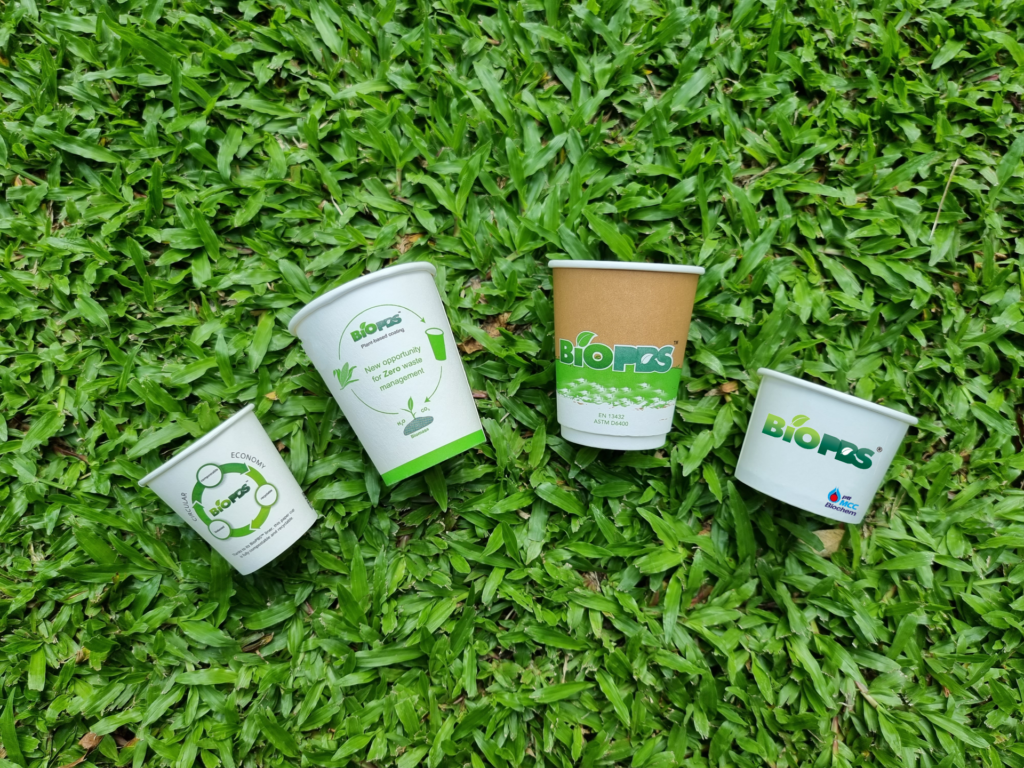

NextGen Cup Challenge winner PTT MCC was selected as one of the market testing solutions for compostable and recyclable paper cups by Starbucks in select stores in Vancouver, Seattle, San Francisco, New York and London. Many other brands have engaged the company to develop more sustainable paper cups solution using BioPBS, the company’s bio-based material for packaging.
4.Capital is accelerating the growth of solutions
Earlier this year, NextGen Cup Challenge winner SoluBlue won the Postcode Lotteries Green Challenge, a global sustainability award and one of the largest annual competitions in the field of sustainable entrepreneurship. Their seaweed-based polymer technology that helps extend the shelf-life of food, reducing both plastic waste and food waste, was selected from more than 650 startups competing from across Europe. The award of €500,000 in prize money will be used by SoluBlue to help scale up their technology for pilot production among retailers.
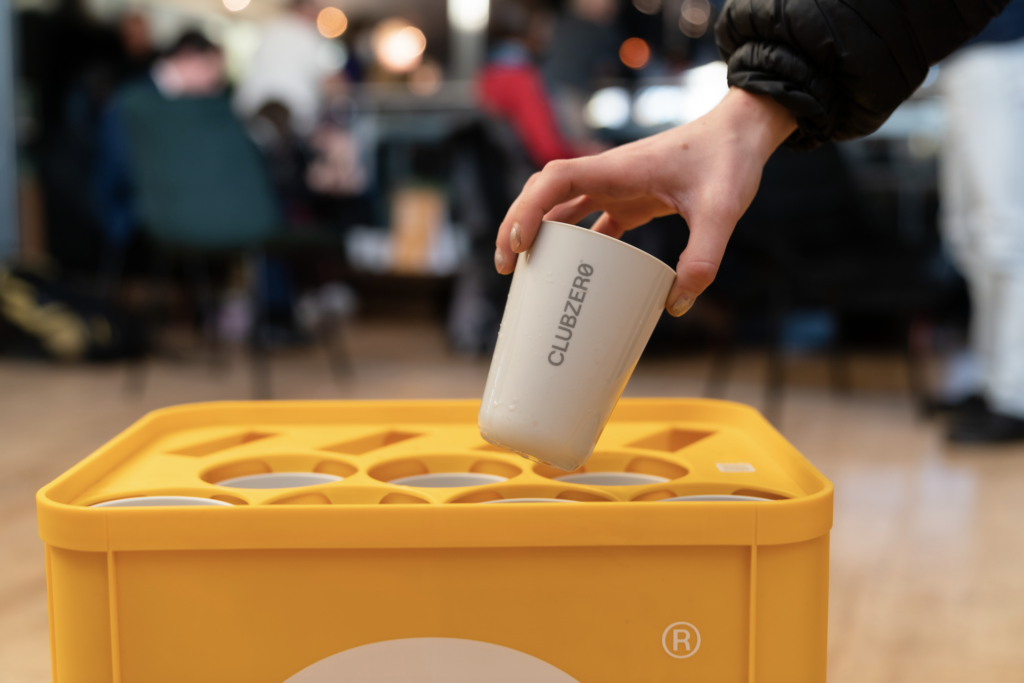

Since winning the NextGen Cup Challenge, CLUBZERØ has gained even more market interest, with more than 380 investors committed to helping their fight for zero waste. Since the launch of their public crowdfunding campaign, CLUBZERØ has to date achieved over 120% of its goal. In September 2021, CLUBZERØ launched their reusable packaging to tackle plastic pollution across the takeaway sector in London, subsequently announcing partnerships with Just Eat, King’s Cross, ReLondon, Camden Council and First Mile. Having completed over 50,000 orders in Q4 2021, CLUBZERØ welcomed new U.S investors including Chris Vance (ex-Tesla + Impossible Foods) and partnered with Nestlé (Nescafé) to provide reusable packaging.
Where do we go from here?
The tremendous gains of these companies show that the road to circular foodservice packaging is being built quickly. Through its grant funding, business acceleration, testing and curated in-market pilots, the NextGen Consortium continues to strengthen the ecosystem of companies, innovators, investors, policymakers and consumers paving the way forward. This is just the beginning of our collective journey, and we are excited for a future in which circular packaging is the standard rather than the exception.