On June 17, 2020, Bridget Croke, Managing Director, at Closed Loop Partners spoke at the United States Senate Environment and Public Works Committee as they held a hearing on “Responding to the Challenges Facing Recycling in the United States.” The following text is drawn from her testimony.
Today, we have over 40 investments in companies and municipal projects in the United States, all focused on helping Americans avoid landfill disposal fees while generating good jobs in the recycling and manufacturing sector. Our investors are a combination of some of the largest American based consumer brands in the world including 3M, Coca-Cola, Colgate Palmolive, Johnson & Johnson, Keurig Dr. Pepper, PepsiCo, Procter & Gamble, Unilever and The Walmart Foundation, as well as the American Beverage Association, institutional investors, family offices and environmental foundations. CLP proves that public–private partnerships are critical to unlocking the capital needed to build robust recycling and circular economy infrastructure needed to create jobs, reduce waste and build the supply chains of the future.
Despite some of the headlines we’ve all seen, recycling is big business in America and should create the manufacturing feedstock for future packaging. In 2019, the recycling industry in America generated over $110 billion in economic activity, $13 billion in federal, state, and local tax revenue and 530,000 jobs. In spite of COVID and market challenges in recent years, 2020 is shaping up to be a year of major innovations in the recycling industry as it becomes central to circular economy business models that major consumer goods companies and cities are deploying. Transitioning US manufacturing to circular supply chains could unlock a $2 trillion opportunity.
Recycling continues to be the most cost-effective option for the vast majority of American cities. The economics are simple. Cities have two choices when it comes to disposal: recycle or landfill. While the value of recycling is generally reported as the amount that a city can be paid for its recyclables, the core economic value of recycling is actually the opportunity for a city to avoid costly landfill disposal fees. Economic analysis conducted has shown that the U.S. scrap recycling industry is a major economic engine powerful enough to create 531,510 jobs and generate $12.9B in tax revenue for governments across the US.
New York City, the largest market in the United States, is an example of how advanced recycling infrastructure and strong local markets create long term profits. New York City has a long-term public-private partnership with Pratt Industries that converts all of its recycled paper locally into new paper products sold back into the NYC market. Via its contract with Pratt, New York City is paid for every ton of paper its residents recycle, as opposed to a cost of over $100 per ton to send paper, plastics and metals to a landfill.
Minneapolis is another good example. Eureka Recycling and the City of Minneapolis invested in local community outreach focused on keeping their recycling stream clean of contamination, defined as non-recyclable material. The result is one of the lowest contamination rates of any municipal recycling program in the country. With a clean stream of valuable recyclables, Eureka consistently shares with Minneapolis the profits earned from the sale of their recyclables. In many other cities, unfortunately, approximately 15% of the material that arrives at the municipal recycling facility is considered contamination. Municipal recycling programs that keep contaminants out of the recycling stream via strong community outreach or enforcement realize lower costs and better revenue opportunities. Municipalities that recognize that recycling is part of the commodities industry, not the waste industry, generate value.
Along with the examples of Pratt Industries in New York City and Eureka Recycling in Minneapolis, Recology in San Francisco and Balcones in Austin, among others, continue to provide their municipal and commercial customers robust recycling service. In addition, municipalities like Pensacola, Florida and Davenport, Iowa that manage their own best in class recycling facilities consistently reduce landfill disposal costs and create local economic value for their constituents.
The value of recyclable commodities continues to have a wide range. The cost to process municipal recyclables at a recycling facility is, on average, $70 per ton. That means that for a recyclable commodity to have value, it must have a market that pays the recycling facility over $70 per ton of that material. A sample of the commodities that are usually profitable to recycle include PET plastic (beverage containers), HPDE plastic (laundry detergent and soap containers), rigid polypropylene (bottle caps, some yogurt containers), cardboard and aluminum.
In 2020, three innovations are driving the increased profit potential of recycling in America and the development of a vibrant and growing Circular Economy.
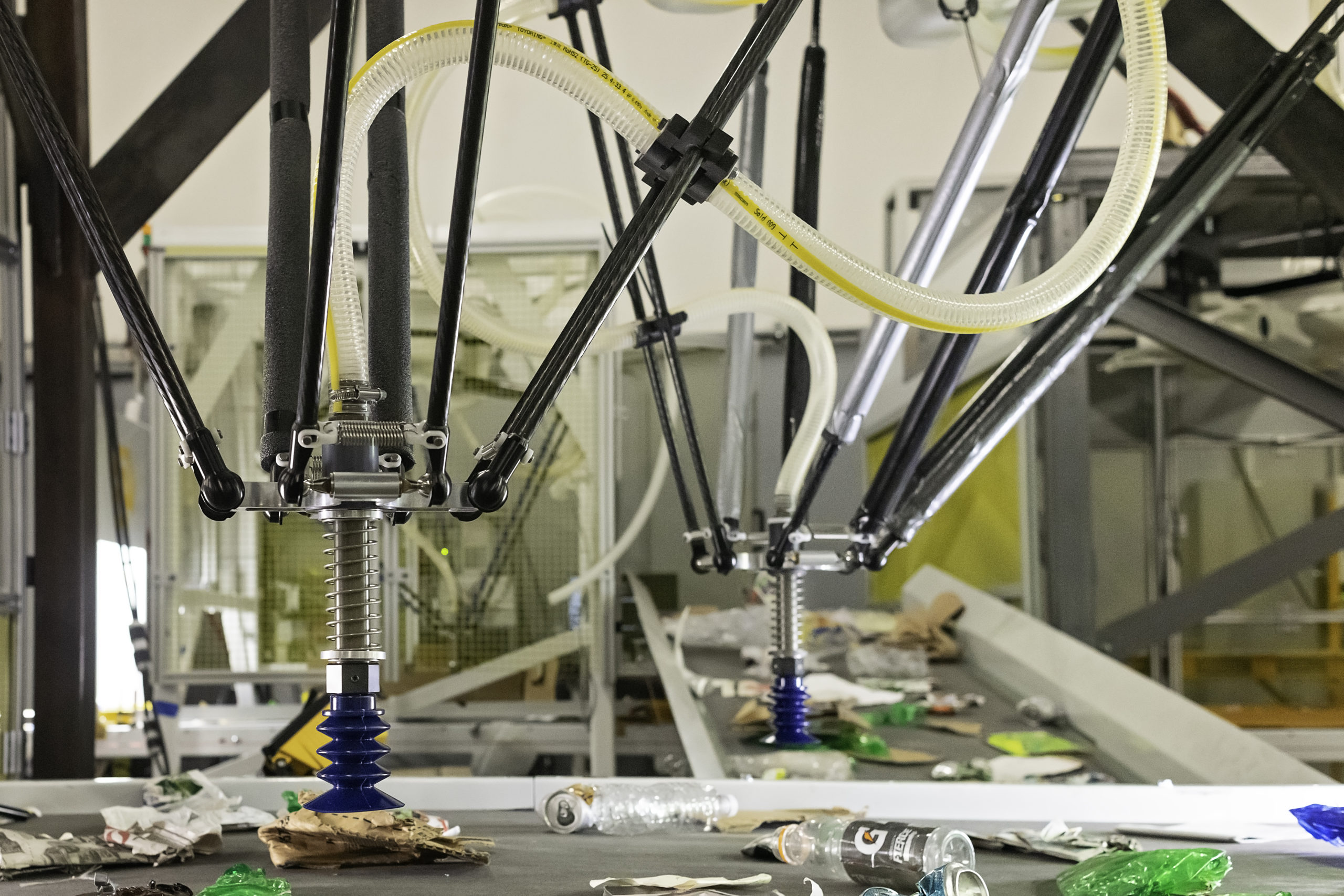
- The introduction of robotics and artificial intelligence. The future of the industry will be led by the recycling facilities that produce the highest quality commodity bales of materials. Companies like AMP Robotics have introduced robotics (robots) with artificial intelligence systems that enable the sorting and production of high-quality commodity bales, supply chain tracking and safeguards against contamination that were never before imagined in the industry.
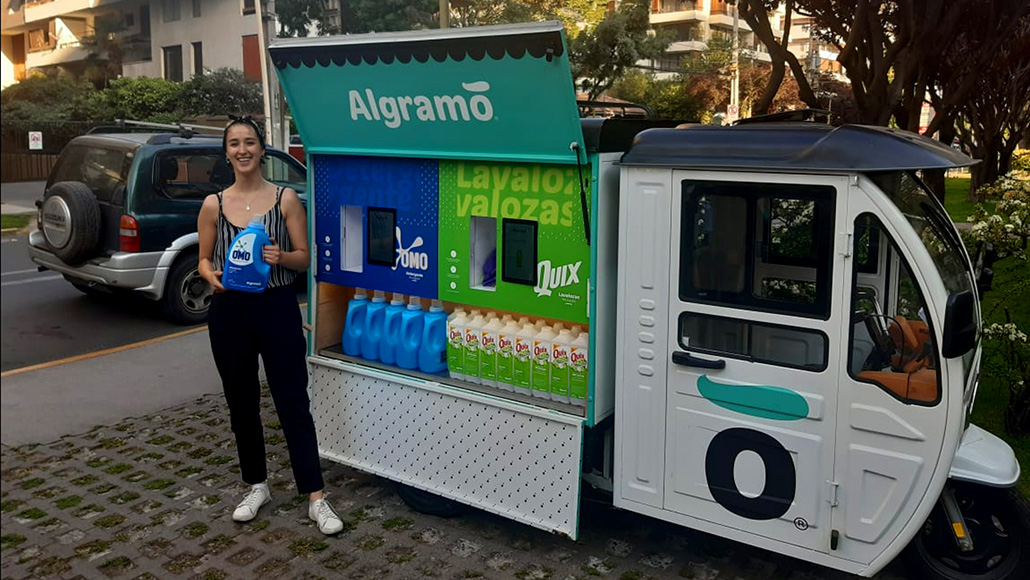
- Packaging innovation. We are seeing the emergence and growth of smart refillable packaging systems like Algramo that makes it cheaper and more convenient for consumers to use packaging more than one time. We are also seeing a growth in packaging that is designed to be recycled for value. Temperpack, for example, is a packaging technology that uses recycled cardboard to keep packaged food cold, replacing a significant amount of low value plastics like Styrofoam peanuts, which are both not recyclable and a common contaminant in the recycling system.
- Advanced plastics recycling technologies, including purification technologies and chemical recycling technologies. Purification is an enzymatic process that improves the quality of recycled plastics so they can more easily be used again in packaging. P&G invented a technology and helped launch a company, PureCycle Technologies, that will significantly increase the value of recycled plastic by removing color and smells. Chemical recycling is a process whereby plastic is depolymerized back to the base monomer, intermediary or carbon state in order to remanufacture a new plastic. Some plastics, like PET, HDPE and rigid polypropylene have significant value and are very profitable for the recycling industry, but they can degrade after a number of recycling cycles while some other plastics currently have limited value or are challenging to recycle. Chemical recycling has the potential to create an infinite circular economy value loop for all plastics. Some of the leading innovators are backed by major consumer goods companies. In 2020, we expect a number of emerging companies to move from pilot to commercialization phase.
These and other circular advancements are attracting significant private capital from leading investors. The industry saw investments from leading investors across asset classes. Google and Sequoia invested in AMP Robotics, Goldman Sachs is now the largest shareholder in Lakeshore Recycling Systems, Citi is largest investor in rPlanet Earth, a bottle-to-bottle plastics recycling facility in California and SJF Ventures invested in TemperPack.
The emerging leadership demonstrated by a number of retailers and consumer brands is driving the growth of the circular economy and improvements in recycling. Leadership means designing products and packaging that are free of any non-recyclable material and profitable for recycling. These packages are manufactured with recycled content, while reducing raw material inputs. Brands are telling their consumers that their commitment is to use recycled content in their packaging. Leaders are transparent in their progress, reporting in their annual reports the use of different recycled feedstocks. They know that any product or package that is not recyclable is destined for a landfill (or even worse, a river or ocean), and that cost is passed to the taxpayer.
Walmart has developed design for recycling guidelines for their suppliers to ensure the products sold in their stores are recyclable and piloting refillable packaging models. Unilever’s Seventh Generation Brand uses mostly recycled HDPE plastic in its packaging and recycled paper in its paper products. And over 10 global companies have invested over $150m in CLP’s investment funds so together we can help spur more innovation and create more tons of recycled feedstock coming through systems in the US.
We are also seeing a major trend amongst consumer goods companies looking to increase their use of recyclable material in the packaging and products they sell. It makes sense. At scale, along with the considerable environmental benefits, it should be less expensive for companies to manufacture using recycled material. That is why most major beverage companies including Coca-Cola, Keurig Dr. Pepper, PepsiCo, Nestle and Danone as well as the world’s largest consumer goods companies such as P&G, Unilever and Colgate Palmolive are publicly communicating aggressive goals for the use of recycled materials in their products and packaging.
For Americans, recycling is a matter of economic self-interest. Recycling our cardboard, paper, beverage bottles, rigid plastics containers, and aluminum cans has three important outcomes. First, it reduces the cost to manufacture the products we buy. Second, it reduces the amount of our taxpayer dollars used every year to pay landfills. Third, it generates revenue for our communities via the sale of recyclable commodities. A recent analysis reported the average cost to dispose of a ton of municipal waste in the US in 2019 was $55 per ton, and disposal fees in some states average more than $100 per ton.
Despite these economic incentives, large parts of the United States still have little or no recycling collection or processing infrastructure. Much of the economic activity generated by recycling is accomplished by long standing recycling programs on the West and East Coast as well as the upper Mid-West of America. For those who live in parts of the country with limited or no recycling infrastructure, their tax dollars are wasted on the cost of sending valuable commodities to landfill that could otherwise be sold. While the 90m tons currently recycled in the United States saves American taxpayers and businesses over $3 billion annually in landfill disposal fees, over 180 million tons of recyclable materials are landfilled, costing American taxpayers and businesses over $5 billion annually in landfills fees. We are literally throwing money in the garbage.
It is also important to recognize how China, which has received much press as of late for their role in the American recycling ecosystem, impacts the industry. For much of the past 20 years, the U.S. recycling industry was dependent on China as the leading export market. As consumption and waste has increased in China, the Chinese government has decided to develop their own domestic recycling infrastructure. This may cause some short-term pain in some parts of the United States’ recycling industry, but leading companies in the recycling industry, consumer goods and packaging industry, as well as a number of investors, see this as an opportunity to further develop and profit from domestic recycling and manufacturing infrastructure.
These are exciting times in the recycling industry as the development of the circular economy continues to expand. Major innovations are entering the industry ranging from robotics to supply chain mapping to advanced technologies that recycle plastics. Like any major industry analysis in the U.S., there is no one or two cities that should be extrapolated to define the industry. There are cities where recycling is profitable and a major economic engine and there are cities where the recycling program is struggling. What is clear is that the cities that focus on limiting contamination in their recycling program, build efficient and effective material recovery facilities and who contract with best in class recycling companies benefit from recycling programs that are both profitable and produce good local jobs.
Leading municipalities, recyclers, manufactures and brands are starting to partner together to establish, and profit from, a circular economy in the United States where goods are continually manufactured using recycled material from local recycling programs. This partnership in developing a circular economy will result in one of the largest investment opportunities in the United States over the next decade, major reduction in landfill disposal fee paid by municipalities, and become a primary driver of job creation in local economies.
We encourage policy makers to build incentives and develop policy to spur the market for recycled content and product and system innovation that reduces waste, creates jobs and makes recycled content competitive with the raw material market.