The Petaluma Reusable Cup Project: Starbucks, The Coca-Cola Company, PepsiCo Lead Brands Launching City-Wide Reuse System in California City
July 09, 2024
The collaboration, led by the NextGen Consortium, makes reusable cups the default option in national and local restaurants across the City of Petaluma.
July 9, 2024, Petaluma, CA –– Starbucks, The Coca-Cola Company, PepsiCo, Peet’s Coffee, Yum! Brands and other global and local brands and restaurants are partnering in The Petaluma Reusable Cup Project from the NextGen Consortium, led by the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners, to activate an unprecedented collaboration to drive reuse. Starting August 5, more than 30 restaurants in the City of Petaluma, CA, will swap their single-use cups for to-go reusable cups to all customers at no cost, and widespread return points will also be available across the city. This program marks a significant milestone for reuse, as the first initiative of its kind that makes reusable to-go cups the default option across multiple restaurants in a U.S. city, with the opportunity to drive more customers to reuse and displace hundreds of thousands of single-use cups.
The Petaluma Reusable Cup Project is focused on supporting customers to create return habits, a key factor to the success of reuse. The city-wide initiative is a critical step forward to catalyze and scale reuse systems, building on half a decade of work by the NextGen Consortium––a collaboration managed by the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners, in partnership with many global foodservice brands.
The mix of large national chains, local independent restaurants, convenience stores, community hubs and public locations makes this initiative distinctly powerful in shaping consumer habits and cultural norms. More than 30 restaurants in the City of Petaluma will be participating in the initiative, including Starbucks and licensed Starbucks cafés in Target and in Safeway, owned by Albertsons Companies; Peet’s Coffee; KFC and The Habit Burger Grill, owned by Yum!; Dunkin’; as well as many local cafés and restaurants. The initiative was made possible through extensive public-private collaboration, with support and engagement from the City of Petaluma, Zero Waste Sonoma, Recology, community groups and local businesses.
“It takes an entire community to build the future of reuse that we want to see,” says Michael Kobori, Starbucks chief sustainability officer. “Our environmental promise is core to our business and that’s why we’re working toward a future vision of every Starbucks beverage served in a reusable cup. Together with fellow foodservice brands, local stores and community stakeholders, we’re leading this initiative to help further unlock behavior change toward reusables, making it easy for our customers, and any customer, to choose to reuse and reduce waste.”
Across the U.S., 50 billion single-use cups are purchased and disposed of each year. Most of these cups are used out of a restaurant and disposed of at home, work or school, with an average lifespan of less than one hour before going to waste, according to the Center for the Circular Economy’s research. While reuse is growing quickly, use of personal cups and existing takeaway reusable cup systems still face low adoption or low returns. For reuse to scale responsibly, it’s imperative to create an easy and enjoyable consumer experience that makes it easy for customers to remember to bring their own containers or to return one that was given to them.
“To create a world without packaging waste, we need to ensure that food packaging reuse systems are scaled in a way that creates a positive environmental impact––meeting the current needs of people while driving a cultural shift toward reuse,” says Kate Daly, Managing Director and Head of the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners. “By testing reuse across an entire city in partnership with key stakeholders from the community and industry, we can scale reuse collaboratively through thoughtful experimentation, building a future where reuse is the norm.”
The City of Petaluma, CA, located in the northern Bay Area, was selected for the initiative for many reasons. In this region, businesses and consumers are receptive to adopting reuse, given the policy environment promoting the phase-out of non-recyclable single-use packaging. The city also participated in a returnable cup test at participating Starbucks locations in 2023. The size and dense layout of downtown Petaluma, with its tight cluster of restaurants and local shops within walking distance, and proximity to suburban and rural areas, creates the right conditions for testing a reuse system for to-go cups. Collaboration with local stakeholders has helped adapt the initiative to local policy and infrastructure, identify optimal return points across the city and engage the broader community.
“The City of Petaluma is laying the groundwork to make cup reuse not only an option, but the default,” says Kevin McDonnell, the Mayor of the City of Petaluma. “We have an amazing, engaged community, and we look forward to assisting the success of this program, alongside our local restaurants and participating global brands that service our community.”
“Imagine a neighborhood where all to-go cups are reusable, and returning these cups required no extra steps. By making reusable cups as convenient and accessible as single use, we can offer an alternative for residents when they forget to bring their own cups with them,” says Leslie Lukacs, Executive Director of Zero Waste Sonoma. “Universal accessibility creates the foundation for a cultural shift towards reuse.”
The Petaluma Reusable Cup Project will install more than 60 cup return bins across Petaluma. After use and return, the reusable cups will be collected, washed and recirculated for future uses by participating businesses and customers. Muuse, a winner of the 2018 NextGen Cup innovation challenge, was selected by the NextGen Consortium to manage all servicing and reverse logistics for the initiative.
“Transitioning to returnable packaging systems is a critical part of reducing single-use packaging waste, and we need to focus on supporting the operations behind it. These systems must be thoughtfully and responsibly implemented to ensure we are minimizing our impact of creating more waste in the process,” says Brittany Gamez, COO & Co-Founder of Muuse. “It is through initiatives like this that we can identify what is needed to operationalize shared systems at this level and inform how reuse is implemented at scale.”
The initiative, which runs until November, will collect baseline data that measures customer participation and the environmental impact of offering reusables as the default choice for customers, testing whether the model is operationally viable for scale. Data from the initiative can be leveraged by businesses and regulators to support them as they design new reuse systems and draft well-informed packaging regulations.
This is another key step in the NextGen Consortium’s longstanding work to advance reuse. Since 2018, the NextGen Consortium, its brand partners and the Center for the Circular Economy ecosystem have been at the forefront of the reuse movement. In 2019 and 2020, the NextGen Consortium launched groundbreaking trials in the San Francisco Bay Area to understand how reusable cup programs might operate simultaneously across multiple restaurants, leading to a foundational reuse report. Starbucks, a NextGen founding partner, has launched cup share programs in over 25 markets globally, including saturation trials in California. They also recently became the first national coffee retailer to accept reusable cups for drive-thru and mobile orders, making significant progress to incentivize customers to bring their own cups to stores. The work to advance reuse also extends beyond the cup. In 2023, the Consortium to Reinvent the Retail Bag, also managed by the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners, wrapped its largest returnable bag program, alongside its largest bring your own bag program, in partnership with CVS Health, Target and other leading retailers.
Moving forward, the NextGen Consortium will continue its work and collaboration with stakeholders from across the reuse value chain, from innovators and activists to global brands and policymakers, to effectively scale reuse systems that are better for the environment.
About the NextGen Consortium
The NextGen Consortium is a multi-year consortium that addresses single-use foodservice packaging waste by advancing the design, commercialization and recovery of foodservice packaging alternatives. The NextGen Consortium is managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy. Starbucks and McDonald’s are the founding partners of the Consortium, with The Coca-Cola Company and PepsiCo as sector lead partners. Peet’s Coffee, with its parent company JDE Peet’s, Wendy’s, Yum! Brands, Delta Air Lines and Toast are supporting partners. World Wildlife Fund (WWF) is the environmental advisory partner. Learn more at www.nextgenconsortium.com.
About the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners
The Center for the Circular Economy is the innovation arm of Closed Loop Partners, a firm at the forefront of building the circular economy. The Center executes research and analytics, unites organizations to tackle complex material challenges and implements systemic change that advances the circular economy. The Center for the Circular Economy’s expertise spans circularity across the full lifecycle of materials, connecting upstream innovation to downstream recovery infrastructure and end markets. Learn more about the Center for the Circular Economy at closedlooppartners.com/the-center/
Does Compostable Packaging Actually Break Down? Composting Consortium Reveals Groundbreaking Findings from Largest Field Test in North America
April 16, 2024
Data in new report reveals that certified food-contact compostable packaging breaks down successfully at commercial composting facilities that meet reasonable operating parameters.
NEW YORK, April 16, 2024 /PRNewswire/ — Today, the Composting Consortium, an industry collaboration led by the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners, released a groundbreaking report that fills a critical data gap for the U.S. composting industry: how well does certified, food-contact compostable packaging actually break down in real-world composting facilities? The report, Breaking It Down: The Realities of Compostable Packaging Disintegration in Composting Systems, shares findings from an 18-month study––the largest known field test of certified, food-contact compostable packaging conducted in North America––revealing the realities of compostable plastic and fiber disintegration in diverse in-field composting conditions.
In total, the study tested over 23,000 units of certified food-contact compostable packaging within large-scale industrial composting environments. This encompassed 31 types of fiber packaging & products and compostable plastic packaging & products––such as PLA and PHA––across 10 diverse composting facilities across the U.S.
The data is released at a critical time, as compostable packaging grows as an alternative to conventional plastics amidst an urgent waste crisis. Roughly one-third of the world’s food is wasted each year––a loss estimated at $230 billion. Nearly 60% of the uncontrolled methane emissions from municipal landfills are caused by discarded food, highlighting its significant impact on the environment. To address the urgent food waste and climate challenge, demand for organics circularity is rising, and with it, the volume of food-contact compostable packaging––a market poised to grow 16% annually in the U.S. until 2032, 4x faster than traditional plastic packaging. Today, the U.S. composting industry is in an early stage of transformation to accept and process more food waste; approximately 70% of the composters who process food also accept and process some format of food-contact compostable packaging, with the understanding that accepting these materials helps bring in more food waste to their facilities.
For compostable packaging to reach its full potential as a circular packaging solution, disintegration at end-of-life is critical, in tandem with consistent labeling and design that differentiates compostable and non-compostable packaging further upstream, as well as policies that incentivize robust composting infrastructure to process these materials. In this new study, the Composting Consortium focuses on how compostable packaging breaks down. Previously, scant information was publicly available on the disintegration of compostable packaging, particularly on the compost environments in which they disintegrate.
This groundbreaking study found that overall, compostable packaging breaks down successfully at composting facilities that meet reasonable operational parameters (e.g., compost pile temperatures, moisture, oxygen, pH, etc., defined in The Composting Handbook). While the Consortium’s study did not assess disintegration with the intention to “pass” or “fail” any specific compostable packaging or product, notably, the average compostable plastic and fiber packaging in-field performance in this study met disintegration thresholds used by industry groups:
- Compostable plastic packaging and products broke down successfully across five composting methods, and all 10 facilities’ varying processing timeframes and operating conditions, achieving 98% disintegration on average by surface area, which exceeds industry thresholds to achieve a 90% or higher disintegration.
- Compostable fiber packaging and products achieved 83% disintegration on average by surface area, meeting industry thresholds to achieve an 80% or higher disintegration. Findings showed that certain operating conditions, like turning, agitation and consistent moisture levels above 50%, support increased disintegration of fiber packaging and products.
The findings point to the viability of certified food-contact compostable packaging as an alternative packaging solution to single-use conventional plastic packaging. It also highlights the importance of ensuring that these materials align with available recovery infrastructure, and the importance of expanding robust recovery pathways to divert compostable packaging, and the food scraps they carry, from landfill––that is at the core of the Composting Consortium’s mission.
The Composting Consortium, in collaboration with its brand and industry partners, the US Composting Council, the Compost Research and Education Foundation and other groups, will leverage these findings to help inform policymaking around compostable packaging, update best management practices for composting facilities and shape a field test standard for evaluating compostable packaging disintegration at composting facilities. Data from this study will be donated to the Compostable Field Testing Program (CFTP), which will later launch an open-source database on the disintegration of compostable packaging. Additionally, ASTM International is currently developing an in-field test method for assessing disintegration of compostable items at composting facilities, and the data from this study will be used to inform the draft field testing method. As the Consortium moves into its next phase of work, the results of this study will shape its engagement and education efforts with composters, municipalities, regulators, brands and packaging manufacturers.
“Field testing for disintegration has been ongoing for three decades, and the Composting Consortium’s work across the value chain has significantly advanced insights for the industry,” says Diane Hazard, Executive Director of the Compost Research and Education Foundation. “The collaborative approach and open-source data from this project both advances field testing methods and equips compost manufacturers and brands with the knowledge to better understand the variability of disintegration across different systems, all major steps towards successfully processing compostable packaging.”
“Brands and manufacturers must prioritize material selection and design and labeling for compostable packaging to achieve optimal performance in composting environments, which can then incentivize composters to accept food-contact compostable packaging materials at their facilities,” says Frank Franciosi, Executive Director of the US Composting Council, an industry partner of the Composting Consortium. “As feedstock for composters becomes diversified and more complex, it’s important for all entities within the supply chain to support consumer education on source separation of organics and reevaluate best management practices to support those composters who choose to accept compostable packaging, and this study is another tool for our industry to be able to start that process.”
“Alongside design and reduction as well as reuse and recycling, composting is an important solution for waste mitigation. Through this research, the Composting Consortium sheds light on what is needed for compostable packaging to have the greatest positive impact. Informed by this robust data, we can together ensure the responsible growth of compostable packaging and composting infrastructure, and drive toward circular outcomes, including increased diversion of food scraps and compostable packaging from landfills,” says Kate Daly, Managing Director and Head of the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners.
The study brought together the Consortium’s corporate brand partners, including PepsiCo, the NextGen Consortium, Colgate-Palmolive, Community Impact at Danaher, Eastman, The Kraft Heinz Company, Mars, Incorporated and Target Corporation; technical partners including the US Composting Council, Resource Recycling Systems (RRS), the Compostable Field Testing Program (CFTP) and the Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI); and a cohort of compost partners including Atlas Organics, Napa Recycling & Waste Services, Specialized Environmental Technologies, Windham Solid Waste Management, Black Earth Compost, Ag Choice Organics Recycling, Happy Trash Can Compost, Veteran Compost and Dayton Foodbank. Advisory partners include 5 Gyres, Foodservice Packaging Institute (FPI), ReFED, the Compost Research and Education Foundation (CREF), the Sustainable Packaging Coalition (SPC), Compost Manufacturing Alliance (CMA), Eco-Cycle, University College London (UCL), Western Michigan University (WMU), University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point and World Wildlife Fund (WWF).
About the Composting Consortium
The Composting Consortium is a multi-year collaboration to pilot industry-wide solutions and build a roadmap for investment in technologies and infrastructure that enable the recovery of compostable food packaging and food scraps. The Composting Consortium is managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy. Learn more about the Consortium at closedlooppartners.com/composting-consortium/
About the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners
The Center for the Circular Economy is the innovation arm of Closed Loop Partners, a firm at the forefront of building the circular economy. The Center executes research and analytics, unites organizations to tackle complex material challenges and implements systemic change that advances the circular economy. The Center for the Circular Economy’s expertise spans circularity across the full lifecycle of materials, connecting upstream innovation to downstream recovery infrastructure and end markets. Learn more about the Center for the Circular Economy at closedlooppartners.com/the-center/
First-of-Its-Kind Study by the Composting Consortium Analyzes Contamination Rates Across U.S. Composting Facilities
February 28, 2024
Commonly held assumptions about contamination were put to the test, revealing new data on the realities of contamination at composting facilities.
February 28, 2024, New York, NY — Today, the Composting Consortium, an industry collaboration led by the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners, released an unprecedented report on compost contamination, Don’t Spoil the Soil: The Challenge of Contamination at Composting Sites. The report reveals first-of-its-kind data on the amount of contamination at U.S. composting facilities, and the significant cost to manage it. Working with composters across the U.S., the Consortium’s in-field study quantifies contamination rates in feedstock and finished compost, highlighting a need for policy, innovation and packaging design to help composters improve contamination mitigation and strengthen organics recovery processes.
The report is released at a critical time for the composting industry, as pressure increases around the growing food waste crisis in the U.S. Today, nearly 40% of food is wasted and sent to landfill in the U.S.––at a loss of $430 billion––and only about 4% of all post-consumer food waste generated by Americans is sent to composters. Organics collection and infrastructure is one key solution to the crisis. To meet growing demand, the U.S. composting industry is shifting. While most composting facilities in the U.S. still only process yard trimmings, curbside organics collection has surged by 49% since 2021. Composter feedstock acceptance policies are also slowly shifting to match demand, with approximately 145 full-scale compost facilities in the U.S. now accepting food waste and some forms of food-contact compostable packaging—that packaging can be a key vessel for diverting food waste to compost, if recovered at composting facilities.
There is eagerness among compost manufacturers to be a part of the food waste solution, but concerns about contamination risks in the organics stream continue to be the one of biggest barriers to greater acceptance of food waste and food-contact compostable packaging. Concerns are increasing amidst the growing volume of compostable packaging in the U.S., largely due to look-alike, non-compostable packaging inadvertently entering the composting stream due to unclear labeling and confusion among consumers. This creates operational and financial challenges for haulers and composters, hindering further acceptance of food waste across the country.
Before the Composting Consortium released this report, there was little to no publicly available data on the amount and types of contamination in feedstock or finished compost products, or the time and money spent by composters to manage contamination at their facilities. To support the composting industry in its transition to accept food waste and food-contact compostable packaging, the Composting Consortium set out to address this data gap by conducting a first-of-its-kind study with 10 leading composters of varying sizes across the continental U.S., capturing a geographically and operationally diverse dataset on contamination volumes and decontamination practices.
The study measures and characterizes contamination across different points of the composters’ processes––and analyzes the financial cost to composters to handle contamination. The study examines five commonly held assumptions about contamination and compostable packaging, and breaks down in-field realities in a data-backed and easy-to-follow format. Key findings include:
- Conventional plastic is the most common contaminant received by composters, making up an average of 85% of the contamination that composters receive, by volume;
- Despite diligent efforts to combat contamination, conventional plastic can persist in the finished compost; 4 out of 10 composters in the study had trace amounts of conventional flexible plastic in their finished compost;
- Contamination has a significant impact on the bottom line; on average, 21% of composter operating costs are spent on contamination removal;
- Most composters had contamination, irrespective of whether or not they accept compostable packaging; several factors contribute to the levels of contamination that a facility receives;
- Eight out of nine composters who accept compostable products in the study had no detectable amounts of compostable packaging in their finished compost.
The data confirms the pervasiveness of plastic contamination, and the need to further mitigate this challenge, both upstream and downstream in the composting value chain. It also highlights that more consistent and standardized compostable packaging design and labeling is needed to ensure that certified, food-contact packaging is properly sorted and recovered at end of life. In the same vein, non-compostable packaging should be distinct in its design and labeling to reduce the risk of conventional plastic packaging making its way into the organics stream. Composters must be supported and incentivized to accept food and certified food-contact compostable packaging, to ensure these materials drive value and circular outcomes to the composting industry.
“Addressing contamination is critical to paving the way for broader organics recovery as a key solution to the food waste crisis in the U.S.,” says Kate Daly, Managing Director of the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners. “The Composting Consortium’s findings shed light on the significant opportunities––and challenging realities––of composting in the U.S. today. This study lays the groundwork for future research and investment to scale end-of-life solutions for food and food-contact compostable packaging to drive circular outcomes.”
This study is an important snapshot of a pervasive challenge that affects the compost industry. This work represents the Composting Consortium’s continued efforts to break siloes and bring together the key stakeholders––upstream, midstream and downstream––to remove barriers and advance a circular economy for organics and compostable packaging. Addressing contamination requires enhancing transparency, intensifying educational efforts and championing innovation. Additional research and collaboration across the entire composting and compostable packaging ecosystem can help pave the way for a circular future, turning food waste into a valuable resource and relieving composters from the burden of contamination.
About the Composting Consortium
The Composting Consortium is a multi-year collaboration to pilot industry-wide solutions and build a roadmap for investment in technologies and infrastructure that enable the recovery of compostable food packaging and food scraps. The Composting Consortium is managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy. PepsiCo and the NextGen Consortium are founding partners of the Consortium. Colgate-Palmolive; Community Impact at Danaher; Eastman; The Kraft Heinz Company; Mars, Incorporated; and Target Corporation joined as supporting partners, and the Biodegradable Products Institute, the US Composting Council and the U.S. Plastics Pact joined as industry partners. Our compost partners for the Contamination Pilot include Ag Choice, Atlas Organics, Black Earth Compost, Dirt Hugger, The Food Bank at Dayton, Happy Trash Can Compost, Napa Recycling, Specialized Environmental Technologies (SET), Veteran Compost, and Windham Solid Waste Management District. Our advisory partners include 5 Gyres, Foodservice Packaging Institute (FPI), ReFED, Compost Research and Education Foundation (CREF), the Sustainable Packaging Coalition (SPC), Compost Manufacturers Alliance (CMA), Eco-Cycle, University College London (UCL), Western Michigan University (WMU), University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point and World Wildlife Fund (WWF). Learn more about the Consortium at closedlooppartners.com/composting-consortium/
About the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners
The Center for the Circular Economy (‘the Center’) is the innovation arm of Closed Loop Partners, a leading circular economy-focused investment firm in the U.S. The Center executes research and analytics, unites organizations to tackle complex material challenges and implement systemic change that advances the circular economy. The Center for the Circular Economy’s expertise spans circularity across the full lifecycle of materials, connecting upstream innovation to downstream recovery infrastructure and end markets.
Closed Loop Partners and the U.S. Plastics Pact Release First-of-Its-Kind Report on Insights from Customers Engaging with Reusable Packaging Systems in the U.S.
January 08, 2024
Key findings support the development of more effective reuse systems that meet customer needs and increase return rates of reusable packaging
NEW YORK – January 9, 2024 – Today, Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy (“the Center”), in collaboration with the U.S. Plastics Pact, published a first-of-its-kind report, Unpacking Customer Perspectives on Reusable Packaging, sharing new insights on customer behavior toward reuse in the U.S. The report seeks to understand customer attitudes, preferences and behaviors around reusable and refillable packaging solutions to help companies, cities and other key stakeholders navigate the current reuse landscape. To effectively address the global plastics waste challenge, we need widespread adoption of reuse systems. Understanding customer preferences is crucial for implementing successful solutions.
Since 2018, the Center for the Circular Economy has been testing diverse reusable packaging solutions in retail stores and restaurants. The Center’s Reuse Insights Lab conducts qualitative and quantitative research and data analytics through in-market testing, focus groups and customer interviews, to identify how to design and build the architecture for a reuse system that brings the circular economy to the forefront in our everyday life. In 2023, the Center’s Reuse Insights Lab collaborated with the U.S. Plastics Pact, engaging the customer bases of 16 innovators participating in the U.S. Plastics Pact’s Reuse Catalyst Program. Based on surveys, interviews and an analysis of hundreds of customers using reusable packaging across the U.S., our methodology focused on early adopter behavior. Rather than asking customers what they would do, we asked them what they already do. This allowed us to avoid the “intention-action gap” that can occur when relying solely on sentiment instead of in-market behavior.
The report shares five key insights distilled from these real-world customer experiences:
- Ongoing education and clear communication are vital to familiarize customers with reuse logistics and enable adoption on a larger scale;
- Technology can simplify reuse tracking—particularly on the backend—but too many tech hurdles on the frontend can overwhelm customers;
- Thoughtful design choices that balance utility, sustainability and appeal are key for reuse systems to achieve their intended impact;
- Choice and availability of reuse options help customers feel empowered to participate; and
- Reuse solutions that meet customers where they are rather than demanding perfection are most likely to support long-term habit formation.
As the Center works to build bridges for reuse systems, we recognize that achieving high return rates for reusable packaging is key to successful adoption. Without high returns, reuse models will struggle to achieve their intended environmental impact. However, with customers at various stages in their reuse journey, building reuse habits takes time. As brands and retailers increasingly look to reuse models as a core sustainability strategy, this timely report provides data-driven guidance on how to successfully scale reusable packaging by understanding customer perspectives and meeting customer needs.
Reuse systems are an essential part of moving away from a linear “take-make-waste” economy towards a system focused on resource circulation. However, to scale reuse sustainably and mitigate unintended consequences of low return rates, solutions must seamlessly integrate into consumer lifestyles and meet customer needs. By reporting on direct feedback from early adopter reusable packaging users, the report provides valuable intelligence on how to optimize participation by assessing real-world experiences, practical applications and perspectives. The insights aim to help both public and private institutions make reuse an accessible, everyday reality.
Kate Daly, Managing Director of Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy notes that, “We’ve reached a crucial moment to make reusable packaging a normal part of everyday life. The research in this report charts a course toward transforming reuse by starting from the customer’s point of view—understanding and overcoming the obstacles people face that stop them from developing a habit of reusing.”
Similarly, Emily Tipaldo, Executive Director of the U.S. Plastics Pact, underscores that, “If businesses and organizations can collaborate to deliver reusable options that truly fit into customers’ lifestyles, reuse can shift from occasional to habitual.”
In the coming year, Closed Loop Partners will release additional insights, building upon this research, as part of an ongoing initiative to accelerate the transition to scalable and durable reusable packaging systems across the U.S. By translating the report’s insights into practical solutions focused on optimizing convenience and value for customers, businesses, advocates and municipalities can propel a culture shift in which reusable packaging models can become the everyday norm.
About the Center for the Circular Economy
The Center for the Circular Economy (‘the Center’) is the innovation arm of Closed Loop Partners, a leading circular economy-focused investment firm in the U.S. The Center executes research and analytics, unites organizations to tackle complex material challenges and implement systemic change that advances the circular economy. The Center for the Circular Economy’s expertise spans circularity across the full lifecycle of materials, connecting upstream innovation to downstream recovery infrastructure and end markets.
The Center’s Circular Insights Lab conducts quantitative and qualitative research and data analytics through in-market pilots, focus groups, iterative testing and consumer interviews, identifying circular trends, challenges and opportunities across multiple sectors and themes, including reuse.
About the U.S. Plastics Pact
The U.S. Plastics Pact is a solutions-driven consortium, launched as part of the Ellen MacArthur Foundation’s global Plastics Pact network. The U.S. Plastics Pact connects diverse public-private stakeholders across the plastics value chain to rethink the way we design, use and reuse plastics, to create a path forward to realize a circular economy for plastic in the United States.
In line with the Ellen MacArthur Foundation’s vision of a circular economy for plastics, which unites more than 850+ organizations, the U.S. Plastics Pact brings together businesses, not-for-profit organizations, research institutions, government agencies and other stakeholders to work toward scalable solutions tailored to the unique needs and challenges within the U.S. landscape, through vital knowledge sharing and coordinated action.
What Brands Need to Know to Increase the Recovery of Compostable Packaging
November 28, 2023
Permitting for composting facilities is complex, but critical. The Composting Consortium breaks it down.
Over the last few years, demand for compostable packaging has grown quickly, as more brands explore alternatives to single-use conventional plastic. Whether in the form of a bowl, fork or a chip bag, compostable packaging is becoming more prevalent each year. At its best, compostable packaging could play an important role in reducing food and packaging waste by helping deliver food scraps within packaging to composting infrastructure, avoiding the greenhouse gases emitted if food were to end up in landfill.
But the reality is that the U.S. composting infrastructure in existence today was predominantly designed to process only yard trimmings––leaves, grass clippings and woody debris––because of a policy trend in the late 80s and early 90s that banned yard waste from landfill in dozens of states. As climate change mitigation and zero-waste goals have emerged, the composting industry is modernizing, diversifying feedstock inputs to include post-consumer food waste and certified compostable packaging. But it is only at the beginning stages of that transition.
The Composting Consortium, a multi-year collaboration across the entire compostable packaging value chain, has been studying composting infrastructure for several years. In the U.S., about 70% of the 200 full-scale composting facilities that process food waste also process some form of compostable packaging. Most of these facilities are located in urban areas. The rest of the over 2,500 composting facilities in the U.S. only process yard waste, meaning most Americans lack convenient options to compost food waste, including food-contact compostable packaging. Creating circular outcomes for compostable packaging hinges on scaling the recovery of food scraps, and brands, packaging manufacturers, industry groups, composters and investors all need to be involved.
What needs to happen so that compostable packaging doesn’t end up as waste?
Several things need to be in place for compostable packaging to operate within a truly circular, waste-free system. Consumer education, supportive policy, and clear and consistent packaging design and labeling all play important roles––and recovery infrastructure is a critical piece to the puzzle.
When envisioning a future system where composting facilities accept not just yard waste, but also food scraps, and the compostable food packaging those scraps often arrive with, the first step is to consider what must be true for facilities to upgrade from yard waste-only composting infrastructure to also recover food.
Only when more food waste is recoverable at composting facilities will it be possible to also see more recovery of food-contact compostable packaging. This infrastructure upgrade is a key steppingstone to reducing packaging waste.
Why do permitting requirements matter?
While there is opportunity to upgrade existing yard trimmings composting facilities to recover food waste––and potentially, also food-contact compostable packaging––it is often difficult to get the necessary permits to do so. In many cases, yard trimmings-only composting facilities are permitted to compost only yard trimmings. To obtain a permit to also compost food waste and make all the necessary upgrades, these facilities would need to go through a lengthy and expensive permitting process.
The Composting Consortium, BioCycle and Craig Croker evaluated each of the 50 states’ permitting requirements across five factors to produce a “Composting Infrastructure Retrofit Score” that measures how easy or difficult upgrading existing yard trimmings-only composting facilities would be across different states.
The final Composting Infrastructure Retrofit Score looked across five factors:
- Ease of permitting process: The difficulty of obtaining a permit to compost food waste in a particular state.
- Presence of permitting tier: Whether a state has rules for composting facilities depending on how much and what types of food waste they accept. Some states have stricter rules for facilities that accept large amounts of food waste or food waste that may be contaminated with pathogens.
- Cost to upgrade: The cost of upgrading a yard trimmings-only composting facility to process food waste.
- Time needed to upgrade: The amount of time it takes to upgrade a yard trimmings-only composting facility to process food waste.
- State food waste disposal ban: Whether a state has a ban or mandate that restricts disposal of food waste.
The findings uncovered a patchwork landscape of permitting conditions across the county as shown in BioCycle’s heatmap below. New York state stood out among the 50 states as having a comparatively straightforward process to obtain permits required for infrastructure retrofit, while most states including South Carolina, Rhode Island and California make navigating permitting requirements significantly more costly and time-intensive.
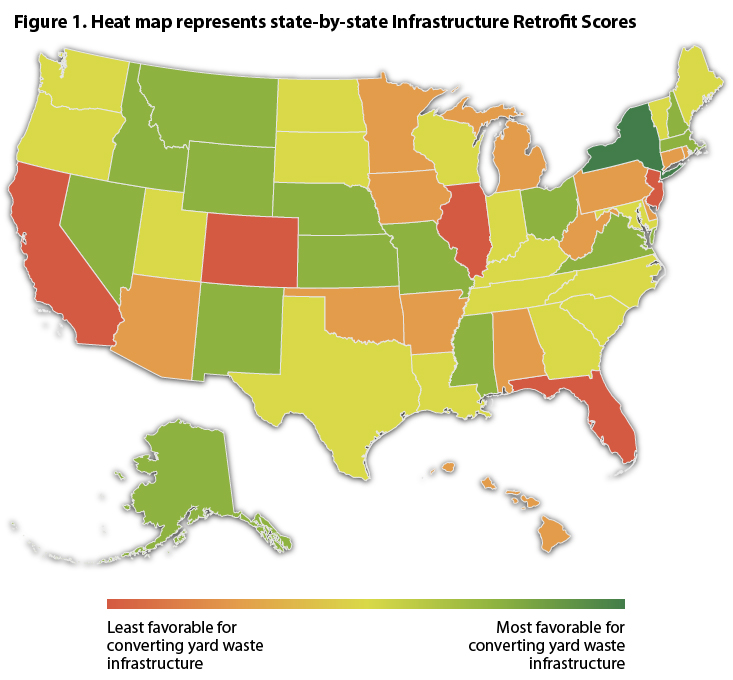
Original Source: BioCycle
In many states, permitting requirements for food waste composting are one of the major factors standing between compostable packaging and the recovery pathways needed to ensure they are a circular alternative to single-use plastic packaging.
What role do brands play in navigating permitting requirements?
CPG brands have a unique opportunity to play a leading role in scaling up a more circular system for food-contact compostable packaging in the U.S.––by investing in recovery solutions for food-contact compostable packaging, advancing consumer education, designing packaging that is compatible with food waste composting infrastructure, and advocating for policies––like extended producer responsibility––that can support the development of food waste composting infrastructure.
To advance the necessary upgrades to composting facilities, brands can be supportive of efforts of composting industry groups like the US Composting Council, who advocates for standardized state regulations for composting. Permitting requirements are a determining factor in creating more opportunities for compostable packaging circularity and navigating them requires the engagement of stakeholders across the value chain.
In 2024 and 2025, the Composting Consortium will continue to connect the dots and work with the compost industry, policymakers, and packaging manufacturers and brands to lower the barriers to scaling food-waste composting infrastructure and unlock value to all stakeholders across the composting value chain. Through this unprecedented collaborative work, the Composting Consortium aims to build a more circular composting system, one that drives values to all stakeholders.
Learn more about the work the Consortium is doing to scale circular outcomes for compostable packaging.
About the Composting Consortium
The Composting Consortium is a multi-year collaboration to pilot industry-wide solutions and build a roadmap for investment in technologies and infrastructure that enable the recovery of compostable food packaging and food scraps. The Composting Consortium is managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy. PepsiCo and the NextGen Consortium are founding partners of the Consortium. Hill’s Pet Nutrition parent company Colgate-Palmolive, Danaher Foundation, Eastman, The Kraft Heinz Company, Mars, Incorporated, and Target Corporation joined as supporting partners, and the Biodegradable Products Institute, the US Composting Council and the U.S. Plastics Pact joined as industry partners. Our advisory partners include 5 Gyres, Foodservice Packaging Institute (FPI), Google, ReFED, Compost Research and Education Foundation (CREF), the Sustainable Packaging Coalition (SPC), TIPA, University College London (UCL), Western Michigan University (WMU), University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point, and World Wildlife Fund (WWF). Learn more about the Consortium at closedlooppartners.com/composting-consortium/
New Report from the NextGen Consortium Shares Path Forward for Paper Cup Recycling in the U.S.
November 01, 2023
Insights include solutions for paper mills, materials recovery facilities, brands and communities to increase recovery of paper cups and reduce waste to landfill
Nov. 1, 2023 — Today, the NextGen Consortium, a leading industry collaboration managed by Closed Loop Partners, with partner brands including Starbucks, McDonald’s, The Coca-Cola Company, PepsiCo, JDE Peet’s, The Wendy’s Company and Yum! Brands, released a report with new findings to accelerate paper cup recycling in the U.S. The report, Closing the Loop on Cups: Collective Action to Advance the Recovery of Paper Cups in the U.S., assesses the role of each stakeholder across the paper cup recovery value chain––including paper mills, materials recovery facilities (MRFs), brands, consumers and local communities––and provides recommended actions to increase paper cup recovery opportunities and advance a more circular system.
Every day, millions of people around the world drink from paper cups. They’re safe, functional and convenient–– so much so that globally, more than 250 billion cups are produced each year. But convenience comes with environmental consequences: the majority of cups end up in landfill today. The NextGen Consortium has taken a three-pronged approach to address cup waste holistically: 1) Advancing reusable cup systems that keep materials in circulation for multiple uses, 2) Exploring material science innovation that enhances the sustainability and recoverability of cup materials, and 3) Strengthening materials recovery and recycling infrastructure that recaptures cups after use.
In this report, the NextGen Consortium focuses on the need to strengthen existing materials recovery and recycling infrastructure systems to recapture more paper cups. Recovering and recycling paper cups ensures the value embodied in paper cups—primarily comprised of fiber and a plastic liner—is recovered, rather than wasted in landfill. These cups contain high-quality fiber that is valuable to paper mills as other paper sources like newsprint and office paper decline. While the challenges for paper cup recovery and recycling are significant, collaboration among various stakeholders involved in paper cup recovery can help address its scale and complexity. The report highlights key challenges and opportunities, including:
- Today, only about 11 percent of communities accept cups in their recycling operations. This poses a significant barrier to cup recycling, as residents have few options to properly recycle their used cups.
- While only a handful of cities in the U.S. are officially accepting cups in their recycling programs, the Foodservice Packaging Institute (FPI) identified more than 30 paper mills that accept paper cups in mixed paper bales representing 75 percent of U.S. mixed paper demand, and an additional five mills accepting cups in carton bales. These mills are taking recovered paper materials, including cups, and reprocessing them into new products.
- In 2023, the NextGen Consortium, in collaboration with FPI and Moore & Associates, identified more than 15 additional mills across North America that are interested in testing cup acceptance or that can process cups today. This new interest is a tremendous endorsement for the work that is taking place and can catalyze cup acceptance at MRFs and in new communities in the months and years ahead.
- Each stakeholder in the value chain has an important role to play in improving paper cup recycling. The report outlines key calls to action, including calling on:
- Mills to conduct recycling tests on paper cups to determine if the fiber can be captured without any negative operational impacts at their facilities;
- MRFs to conduct material flow studies to determine where best to site interventions for cup sortation and to collaborate with mills and communities to expand acceptable recycling lists as more mills accept cups;
- Communities to engage with MRFs and mills to evaluate feasibility of adding cups to accepted recyclables list;
- Consumers to bring their own reusable cups when they can and to check local recyclability options and guidance when using disposable cups;
- Brands to source recycled paper content when procuring their cups and other packaging, among other activities.
“The waste generated from to-go paper cups has become a highly visible representation of our disposable, take-make-waste culture. However, these cups also are a valuable resource with growing opportunities for recovery,” says Kate Daly, Managing Director and Head of the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners. “We know that collaboration across stakeholders––from mills and MRFs to brands and cities––is going to be critical to solving this challenge and ensuring paper cups don’t end up in landfill or polluting our environment. The NextGen Consortium plays a key role in advancing the innovation, testing and partnerships needed to make this possible.”
Since its founding in 2018, the NextGen Consortium has taken a holistic and collaborative approach to addressing the challenge of single-use cup waste, advancing reuse models, exploring material science innovations and strengthening materials recovery and recycling infrastructure that recaptures cups after use. While material reduction and reuse are key pathways to reduce reliance on virgin resource extraction, end-of-life recovery pathways are equally critical to ensure that the value embodied in all types of cups, including single-use paper cups, is recovered, rather than wasted in landfill.
As the NextGen Consortium works toward its goal of eliminating foodservice packaging waste, it will continue to work to improve and align recovery and recycling infrastructure across the entire value chain, from collection and sortation to processing and strengthening end markets. Collaborative action, data-driven decision-making and iterative testing continue to be critical to closing the loop on a greater diversity and volume of valuable resources and avoiding unintended consequences. The learnings from this report aim to guide the industry towards a future in which reusing valuable materials in products becomes the commonsense norm, shaping a more circular economy.
About the NextGen Consortium
The NextGen Consortium is a multi-year consortium that addresses single-use foodservice packaging waste globally by advancing the design, commercialization and recovery of foodservice packaging alternatives. The NextGen Consortium is managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy. Starbucks and McDonald’s are the founding partners of the Consortium, with The Coca-Cola Company and PepsiCo as sector lead partners. JDE Peet’s, The Wendy’s Company and Yum! Brands are supporting partners. The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) is the environmental advisory partner. Learn more at www.nextgenconsortium.com.
About the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners
Closed Loop Partners is at the forefront of building the circular economy. The company is comprised of three key business segments: Closed Loop Capital Management, the Center for the Circular Economy and Circular Services. In 2018, Closed Loop Partners launched its innovation center, the Center for the Circular Economy, which unites competitors to tackle complex material challenges and to implement systemic change that advances the circular economy. Closed Loop Partners brings together designers, manufacturers, recovery systems operators, trade organizations, municipalities, policymakers and NGOs to create, invest in and support scalable innovations that target big system problems. Learn more about the Center’s work here.
Reuse
When Reusable Cups Reach End-of-Life: 5 Tips to Ensure They Don’t Go to Waste
October 18, 2023
We know reuse plays a critical part in reducing foodservice packaging waste. And we’ve seen progress and innovation across all types of packaging and foodservice venues, whether cup share programs, reuse at concerts and events, or even for food delivery services. However, for reuse models to be successful and impactful, they need to check a lot of boxes––they have to fit the lifestyle of customers and align with the reality of retail operations to ensure reusable packaging is sufficiently reused. They also have to be recyclable so that they don’t become waste when they end up somewhere other than the return bin at any point in their lifecycle. Whether a reuse program has a 95 percent (terrific!), 75 percent (needs improvement) or 25 percent (look out!) return rate, designing for recyclability is key, especially as more reusable packaging enters the ecosystem. Appropriate end-of-life management is necessary to maximize the intended environmental benefit that reusable products offer.
Since 2018, the NextGen Consortium has been leading efforts to identify the role reuse can play in addressing foodservice packaging waste, alongside material innovation and recovery [see: Bringing Reusable Packaging Systems to Life: Lessons Learned from Scaling Reusable Cups]. In addition to examining the realities of consumer behavior and retail operations when deploying reuse systems, one critical question we recently investigated is: what happens when a reusable cup ends up in the recycling system?
Reusable foodservice packaging is often designed for durability––both in how long it can be reused and how many times it can be washed––but not always for recyclability. As a result, when reusable cups are decommissioned, or end up anywhere but the reuse bin, they inevitably end up in our waste streams. From NextGen’s consumer research, we know that unless disposal options are convenient, these cups will likely end up as waste. Designing reusable packaging for both consistent reuse and eventual recyclability will help increase recovery opportunities and reduce waste to landfill and the environment.
How do we ensure reusable cups do not become waste when they can no longer be reused or end up in a recycling bin rather than a reuse bin?
Testing is key. There are excellent design guidelines, such as APR’s design for recyclability guidelines, to help suppliers ensure their packaging meets the stated needs of the recycling system today. But reusable cups also need to be tested within the recycling process to see if they can be successfully recovered. There are three critical stages of the recycling process:
- Collection: how recyclable materials are collected in residential or commercial waste streams
- Sortation: how a package will flow at a material recycling facility (MRF)
- Reprocessing: how a package aligns with similar materials to be processed and remanufactured into new materials
In early 2023, the NextGen Consortium collaborated with Van Dyk Technology Center to test how a dozen different reusable polypropylene (PP) cups would sort within a MRF and see if they would end up in the correct material bale, in this case PP.
The test mimicked the flow of a typical MRF, followed APR’s sorting guidance and tested how size, compression, 2D and 3D sortation, and near infrared (NIR) sortation impact how well a cup can be sorted. The results were mixed and provide critical design insights for the companies who are manufacturing and deploying reusable cup formats.
The Results: the good, the bad and the unrecyclable.
When designed with recycling in mind, a reusable PP cup should successfully sort into the correct bale at a MRF. In our tests, the top four best performing cup models were sorted correctly more than 90 percent of the time. The test ran 50 samples of each cup through four separate runs so that each cup model ran through the facility 200 times. The results are no coincidence: successful sortability was driven by specific factors, including color, shape, opacity, thickness and material composition. The highest performing cups were typically opaque, thin and rigid but had some flexibility or bounce, and were all read clearly by the optical sensors of the sortation equipment. Cups that performed poorly, sorting less than 50 percent of the time (or sometimes not at all), often were more translucent than their successful counterparts. Overall, while only four of the cups achieved successful sortation (and a fifth cup was borderline), simple design corrections can improve the fate of the others.
Design Tips: Making recyclability a priority for reusable PP cups.
The Van Dyk sortation test gave a window into what happens to various types of reusable PP cups traveling through a MRF. However, this only assessed one step in the recycling process––sortation––and does not confirm compatibility with reclamation systems nor prove that the cup can be recycled effectively into a new package. Additional testing is needed to confirm assumptions that reusable PP cups are truly circular. For now, reusable foodservice packaging companies and suppliers can design with sortation in mind and improve end-of-life outcomes by considering the following:
- Follow the design guidelines created by APR and other groups: There are many resources available online to help packaging designers/suppliers ensure greater compatibility with the recycling system. For plastic packaging, the APR Design® Guide is a great place to start.
- Avoid all black plastics: While there have been technological advancements to help sort black plastics, most MRFs do not possess that technology. Both opaque and translucent black packaging is problematic and reusable cup manufacturers should design cups with today’s system in mind. If black is absolutely required, use an NIR sortable black colorant. Colorants that have passed APR testing can be found on APR’s website here.
- Not all polypropylene is equal: PP is a wide class of material. PP sorters in the recycling process are designed to detect and separate PP that is common to single-use plastic such as tubs and lids; however, other PP grades may not be as easily identified.It is critical to engage with your cup suppliers and test if needed to confirm compatibility.
- Mono materials (cups made of just one material) are best: A reusable cup that is multi-material (i.e., part plastic, part fiber, part silicone, etc.) is simply not compatible with today’s recycling system. Cups designed to be in a high-volume sharing system should be made of a singular material and avoid too many add-ons. Cups with ridges (i.e., a built-in sleeve) may also impede sortation; however, it does not appear that those design features are overly detrimental.
- Think twice before adding tech: Tracking systems are typically needed to assess the impact of a reuse system and enable traceability, but features such as Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags need to be evaluated further for their impact on the recycling system. While an RFID tag is unlikely to hinder a package’s sortability, it might impact whether a material can be reclaimed or recycled. APR’s guidance lists RFID tags as “detrimental,” and the NextGen team is investigating the impact this technology has on the system.
When in doubt, TEST.
Despite widely available design guidance, reusable packaging that is not compatible with today’s recycling system continues to be manufactured. The conversation needs to be more nuanced and shift from only discussing designing for durability and the number of washes a package can withstand, to the realities of how the packaging will actually be used and travel through a system. Most reusable wares in an open system would be lucky to hit 40 reuses (which would assume a >95% return rate)! Sortation and recovery testing can help provide reusable foodservice packaging companies with additional peace of mind and ensure that their packaging has a better chance of staying out of landfill.
The NextGen team looks forward to continuing this journey to study and test optimal conditions for reusable packaging to succeed and achieve a positive environmental impact within a circular economy.
How a South Carolina Paper Mill Started Recycling Your Paper Coffee Cups
September 26, 2023
A spotlight on Sonoco and its recycling tests with the NextGen Consortium
In July 2022, Sonoco announced it would accept paper cups in bales of mixed paper at its paper mill in Hartsville, South Carolina. The NextGen Consortium supported cup trials with Sonoco. Below, we discuss with Scott Byrne, Director, Global Sustainability Services at Sonoco how the organization made this decision and what considerations companies might want to take when exploring the recyclability of different types of packaging.
This work represents part of a forthcoming report on paper cup recovery in the United States intended for release in late fall.

Scott Byrne, Director, Global Sustainability Services at Sonoco
1. Who is Sonoco and what are you focused on?
Sonoco is a South Carolina-based global packaging company with more than 20 mills worldwide. Among our packaging products, we manufacture rigid paper cans, steel cans, thermoformed plastics and other packaging formats. Sonoco is uniquely positioned as a leading recycler, paper mill operator and paper packaging converter, in addition to other formats, to help push the industry to look towards future innovations and grow end-of-life solutions across the entire paper value chain.
2. How do you typically approach recycling of new products at your mills?
After validating that our mills could recycle rigid paper cans in residential mixed paper, we decided to further demonstrate the ability to recycle other similar polycoated fiber-based containers through the post-consumer mixed paper stream.
3. Where do you currently accept paper cups?
Hartsville, South Carolina. and we are exploring other Sonoco mills as well that use residential mixed paper.
4. What are some of the steps you took to determine that accepting cups wouldn’t create new challenges for your mill?
With support from the NextGen Consortium, we conducted two main activities to assess how cups might behave. First, we conducted lab-based testing of both single- and double-sided poly-coated fiber cups. Second, and after we were confident that the cups would not pose any issues to our equipment, we ran a large-scale trial whereby we dosed in nearly 20 tons of cupstock and cups into our pulper alongside other mixed paper, increasing the volume relative to other materials to test the system and upper bounds of materials we’d anticipate receiving if we accepted cups. Based on those results we felt confident that cups could be included in our accepted materials list and we were thrilled to have the mill listed alongside others on Foodservice Packaging Institute’s end market map of mills that accept cups.
5. What about your other paper mills?
Before we broadly accept cups at more of our mills, we’d want to distill our findings from the Hartsville location and consider any additional steps those mills would need to take to feel confident in accepting cups. This might include additional lab-and mill-based trials.
6. Any advice you’d give to other mills considering including cups?
Every mill is slightly different, from their equipment to operating conditions to inbound material mix. Testing to those conditions is a key proof point in determining what might work best in that location.
7. What’s next for Sonoco in its efforts to improve polycoated paper recycling?
Sonoco is a founding member of the Polycoated Paper Alliance that kicked-off in March 2023, which aims to increase widespread end-market acceptance of polycoated paper packaging products. We are collaborating with like-minded member brands and industry leaders on developing improved and harmonized data, updated design guidelines, expanded end market acceptance and upgraded mill specifications, among other initiatives.

How AI Could Change the Way We Think About Recycling
September 11, 2023
Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy and the NextGen Consortium launch a new study with AI technology company Greyparrot to analyze the composition of polypropylene in recycling streams
Behind the walls of recycling facilities across the U.S., a sea of materials moves through hands and machines working hard to get them to the end of the line––and the beginning of their next life. A critical balance of manual labor and automation enables the sorting and recovery of these materials in a closed loop system. Yet despite a multi-step sortation process, it is difficult to track what flows through the system at all times. It’s a challenge that results in many recycled materials losing potential value, in addition to millions of dollars worth of valuable material being sent to landfill unintentionally.
Among the diverse materials flowing through the recycling system are the yogurt containers, and iced coffee and fountain beverage cups many of us use on a regular basis. These are just a few examples of products made of one of the most commonly used resins in foodservice packaging today: polypropylene (PP). PP is a valuable material that should be kept in circulation to reduce waste and meet corporate commitments to use more recycled content in foodservice packaging. With that said, very little mechanically recycled food-grade PP actually cycles back into food-grade applications. Most end up in nonfood-grade applications that limit their value and the number of times they can be reused. To create a more circular path for food-grade PP, we must first answer the question: what is in the PP stream today, and how much of it is food-grade or clear food-grade PP?
The NextGen Consortium is a multi-year industry collaboration addressing single-use foodservice packaging waste by advancing solutions across material innovation, reuse and recovery infrastructure––and it’s working to answer that question. In the fall of 2022, the Consortium partnered with Resource Recycling Systems to examine PP bales in two materials recovery facilities (MRFs) to learn what was inside. While only a snapshot in time, the results were enlightening.
On average, nearly half of the PP bales (48%) were presumed food-grade, and more than a quarter of the bales were clear food-grade (26%). Clear beverage cups represented 14% of the bale on average. The high percentage of food-grade PP suggested that there is untapped value in the PP stream. A better system is required to ensure food-grade and/or clear food-grade PP is properly sorted into a separate bale at some point in the value chain if we are to retain its highest potential value.
This year, the NextGen Consortium is diving even deeper, launching a first-of-its-kind study leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze the composition of the PP material stream well before it ends up in a bale. Together with its managing partner––Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy––the NextGen Consortium is working with Greyparrot, a leading AI waste analytics platform for the circular economy. The collaboration aims to track and categorize objects in the PP stream, and determine the volume of valuable food-grade material passing through the system. AI is on the rise as one potential means of increasing visibility into the recycling process. Today, more technologies are needed to handle an increasingly mixed stream of collected materials, including plastics, electronics, textiles and food scraps––and to enable the recovery of clean, high-quality materials.
“Ensuring that recovery infrastructure can keep pace with a rapidly growing and diverse material stream is critical to advancing the circular economy, alongside solutions such as material innovation, reduction and reuse,” said Kate Daly, Managing Director and Head of the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners. “An important part of our work in the NextGen Consortium is identifying opportunities for data collection and analysis that can advance the circularity of foodservice packaging, and drive greater value for stakeholders across the system, including brands, innovators, infrastructure operators and consumers.”
As part of this project, the Greyparrot Analyser units will be installed above the PP recovery conveyor belts at four leading U.S. MRFs: Balcones Recycling, TX; Cougles Recycling, PA; Rumpke Recycling, OH; and Eureka Recycling, MN. Greyparrot’s AI-powered computer vision system uses cameras to capture images of objects in the PP stream, aiming to quantify and qualify the materials flowing through the MRFs. Their AI model will look to categorize each object based on material, format, financial value and brand, as well as distinguish food- and nonfood-grade material, using those images. Their units will then send that data to an analytics dashboard in real-time. Through machine learning, the flexible vision systems can help improve their package recognition and classification over time.
“We use artificial intelligence to gain continuous and reliable visibility into recycling streams,” said Ambarish Mitra, Co-founder and CPO of Greyparrot. “This helps us improve recycling operations by placing waste intelligence into the hands of the people who are recovering, redesigning and remanufacturing the objects we throw away. We are thrilled to work with our U.S. partners towards our vision of a future where every piece of waste is valued as a resource.”
The collaborative project––a first of its kind in North America––will run for more than six months. During that period, it will gather data on the composition of PP bales over time, while accounting for seasonality. That insight can help determine the potential untapped value in these streams, and identify other materials that might be coming through unintentionally. This data can also help shed light on the presumed volume of food-grade material being captured in the system, along with opportunities for recovery and separation into distinct value chains. More broadly, this can advance a circular economy for valuable materials, improve material quality delivered to recycling facilities, and enhance the value of recyclable commodities shipped to U.S. end markets.
“A lot is unknown about the curbside polypropylene stream today. Filling these knowledge gaps can increase the pace of development for material recovery. Understanding the composition of the stream in a large-scale study highlights potential, reduces risk for pioneers and accelerates better design implementation. This study will be the catalyst to developing much larger-scale recycling of polypropylene,” said Curt Cozart, President of Common Sense Solutions and Technical Advisor to the project.
PP cup recovery––alongside material innovation, reuse and fiber cup recovery––is a critical focus for the NextGen Consortium. According to The Recycling Partnership, more than 2 billion pounds of PP are generated every year by single-family households in the U.S. If just 30% of this material were recovered, it would reduce greenhouse gas emissions by over 300,000 metric tons, providing over 600 million pounds of valuable raw material to companies with recycled content commitments for their foodservice packaging, both voluntary and mandated.
The NextGen Consortium has been actively involved in PP recovery since 2021, when it joined The Recycling Partnership’s Polypropylene Recycling Coalition as a Steering Committee member. Through this initiative, the group helps to fund equipment grants for MRFs so that they can effectively capture PP packaging, and improve community recycling access rates. In addition to improving recycling access, the NextGen Consortium is committed to driving recycling rates by supporting the recovery of post-consumer recycled content (PCR) that can be re-incorporated into packaging.
This collaboration with Greyparrot and MRFs across the U.S. is one critical step toward achieving the NextGen Consortium’s goals. As more data about the PP material stream is captured over the next six months, the Consortium will analyze the new data, identifying opportunities to improve PP sortation and recovery into higher value, new food-grade applications and areas where more research is needed. The NextGen Consortium continues to invite additional MRFs to participate in the project, to gain a better understanding into what is flowing through their material streams and identify ways to drive more value to the system.
About the NextGen Consortium
The NextGen Consortium is a multi-year consortium that addresses single-use food packaging waste globally by advancing the design, commercialization, and recovery of food packaging alternatives. The NextGen Consortium is managed by Closed Loop Partners’ Center for the Circular Economy. Starbucks and McDonald’s are the founding partners of the Consortium, with The Coca-Cola Company and PepsiCo as sector lead partners. JDE Peet’s, Wendy’s and Yum! Brands are supporting partners. The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) is the environmental advisory partner. Learn more at www.nextgenconsortium.com.
About the Center for the Circular Economy at Closed Loop Partners
Closed Loop Partners is at the forefront of building the circular economy. The company is comprised of three key business segments: Closed Loop Capital Management, the Center for the Circular Economy and Circular Services. In 2018, Closed Loop Partners launched its innovation center, the Center for the Circular Economy, which unites competitors to tackle complex material challenges and to implement systemic change that advances the circular economy. Closed Loop Partners brings together designers, manufacturers, recovery systems operators, trade organizations, municipalities, policymakers and NGOs to create, invest in, and support scalable innovations that target big system problems. Learn more about the Center’s work here.
Reuse
Making Reuse an Everyday Reality: 3 Things We Must Consider Before Scale
September 06, 2023
Reuse is now at a critical stage of development. A plethora of innovation has expanded the realm of possibilities, but what will it take to get to the point of industry-scale disruption?
Earlier this year, seven winners of the highly anticipated 2023 Reusies were announced on stage at GreenBiz’s Circularity23 Conference in Seattle. The winners encompassed corporate and community initiatives, and B2B and B2C reuse innovations across food & beverage, consumer packaged goods and fashion & apparel. Together, they provided a window into the best and brightest developments in the reuse space. Indeed, hundreds of start-ups and large corporates are working on making reuse an everyday reality for consumers, with applications as far-ranging as closed system solutions for corporate campuses and events, to software companies supporting reuse-as-a-service, and refill applications in retail or in commercial, industrial and event spaces. The potential for reuse to reduce waste has catalyzed much innovation and brought conversations to a fever pitch.
Reuse is now at a critical stage of development. A plethora of innovation has expanded the realm of possibilities, but what will it take to get to the point of industry-scale disruption? Making reuse a far-reaching and everyday reality––where reusable items are consistently and efficiently reused to make a significant difference and reduce environmental impact––requires continued testing, collaboration across the value chain, investment and supportive policy.
At Closed Loop Partners, reuse systems are an integral part of our vision of a transition away from the take-make-waste economy and toward a circular economy. When products that have historically been single-use are able to be used two, five, ten or one hundred times, and the proper recovery infrastructure is in place for their eventual end-of-life, that can make a meaningful difference on reducing valuable materials sent to landfill––and on the embodied carbon, water and materials required to produce the item in the first place.
But to get to this next horizon, a number of factors must be considered to ensure that reuse does not result in unintended consequences and instead serves a truly circular economy:
1. Closed or semi-closed reuse systems are a key starting point, especially at early stages of adoption. On-premise reuse unlocks higher return rates which can make reuse systems profitable––or at least breakeven. In open systems, as consumers use and dispose products away from point of adoption, more complex collection networks and communication strategies are needed to drive returns. For this reason, closed systems can operate with lower upfront capital expenditures and lower recurring operating expenditures until the time at which consumer behavior has shifted to be more amenable to open systems (see #3!).
2. Reuse is a hardware-first business, and requires capital and collaborations to build localized infrastructure––including collection, sorting and washing. There continues to be a shortage of washing infrastructure needed for reuse solutions, and traditional waste management players are not currently set up for the type of collection and sorting needed for reusable products that are intended to stay in circulation for more than one use. Many software-only solutions still require partnerships with washers and logistics providers. There is an opportunity for founders, corporates and municipal governments to build out these partnerships to enable reuse and share in the funding that will be required to build this new infrastructure.
3. Broad consumer adoption starts with meeting customers where they are today. There are still many customers that have yet to be onboarded into the reuse culture. As we’ve seen in our work through the Beyond the Bag Consortium and the NextGen Consortium, we need to design solutions with current behaviors in mind and support customers as they build new habits. Advancing reuse won’t happen overnight; cross-industry and cross-company collaboration, a range of solutions, clear messaging and consistent regulatory frameworks are required to effectively support consumers in adopting reuse within their communities, as the industry addresses complex waste challenges. Importantly, in-market testing plays a key role in unlocking what works effectively in the market and meets customer needs. Today’s market is complex, with diverse customer demographics and shopping habits, different operations across retailers, a range of reuse packaging materials and more that need to be considered.
We see experimentation as a critical precedent to scale. Reuse is no simple feat, and testing market fit and operation alignment is an important step to expand reuse responsibly and mitigate unintended consequences that can happen without a measured examination of new systems. But isolated, small-scale experiments will not get us there. Closed Loop Partners runs multi-brand reuse tests through its Center for the Circular Economy to identify tactics that are proven and ready to scale, as well as models that require further tweaking and iteration to deliver the expected environmental and financial outcomes. While we work to scale proven solutions, we continue to de-risk systems that need refinement. Our in-field deployments intentionally mimic large-scale, cross-brand implementation, but in a controlled manner. The insights and data gleaned from these tests are key stepping stones to new rounds of implementation and scale. Most recently, the Beyond the Bag Consortium’s largest multi-brand reusable bag pilots tested a range of reuse solutions to understand what it will take to effectively drive reduction of single-use plastic bags. Next year, the NextGen Consortium will go back into market to test the viability of reusable cup systems across multiple brands. These tests unlock important insights on what it will take to build a culture of reuse and will serve as the foundation for identifying scalable initiatives.
With all these developments, we believe we’ll get there. There are tremendous tailwinds supporting the development of reuse and a multitude of communities, innovators and corporations committed to seeing the shift through. To do so, the next five years are critical to pivot from bespoke solutions to shared frameworks, from ad hoc consumer engagement to a consistent drumbeat, and from in market tests to truly scaled solutions. We are excited to be working to advance the transition from innovation to scaled solutions that can replace single-use. Join us!
This article represents perspectives from across Closed Loop Partners, including the Center for the Circular Economy and Closed Loop Capital Management. Special thanks to Kate Daly, Carol Lobel, Danielle Joseph, Aly Bryan and Anne-Marie Kaluz for sharing their thoughts for this piece.
